IT Course JavaScript Basics 036_Syntax Structure
Statements
JavaScript statements are a set of instructions used to perform specific tasks.
Example:
// Variable declarationlet userName = 'Zhao Jian';let age = 18;
// Conditional statementif (age >= 18) { console.log(userName + ' is an adult');} else { console.log(userName + ' is a minor');}
// Loopfor (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) { console.log('Loop output ' + (i + 1));}
// Function definitionfunction Hello(name) { return 'Hello, ' + name + '!';}
// Function calllet sayHello = Hello(userName);console.log(sayHello);Semicolons
In JavaScript, the semicolon (;) is a statement terminator used to identify the end of a statement. Semicolons are optional in most cases because the JavaScript interpreter attempts to automatically insert semicolons (Automatic Semicolon Insertion, ASI) to make the code parse as syntactically correct. However, there are cases where ASI may cause unexpected behavior, so it is recommended to explicitly add semicolons when writing JavaScript code.
When a semicolon appears, whether on a single line or multiple lines, the statement ends.
Example:
alert('Hello');alert('JavaScript!');When there is a line break, in most cases you can omit the semicolon.
Example:
alert('Hello')alert('JavaScript!')alert('Hello');alert('JavaScript!')alert('Hello')alert('JavaScript!');alert('Hello');alert('JavaScript!')When encountering statement blocks or code blocks, line breaks do not automatically add semicolons. Also, spaces and line breaks are ignored.
Example:
alert(1+ 2 +1);Comments
In JavaScript, comments are text used to add explanations and notes in the code. These texts have no actual impact on program execution. Comments are very useful for improving code readability, collaboration, and debugging.
Single-line Comments
Using the // symbol creates a single-line comment. All text from // to the end of the line will be treated as a comment.
Example:
alert('Hello JavaScript!'); // Single-line comment following the statement// Single-line comment on its own lineMulti-line Comments
Using /* to start and */ to end creates a multi-line comment. All text between these two symbols will be treated as a comment.
/* This is a multi-line comment that can span multiple lines*/alert('Hello');/*Multi-line comments can also be used to comment out a block of code, the code below will not executealert('JavaScript!');*/Dialog Boxes
JavaScript provides several dialog boxes for simple interaction with users, including alert, confirm, and prompt. These dialog boxes allow you to display information to users, ask questions, or accept input. When a dialog box is displayed, code execution pauses until the user closes the dialog box.
alert Dialog Box
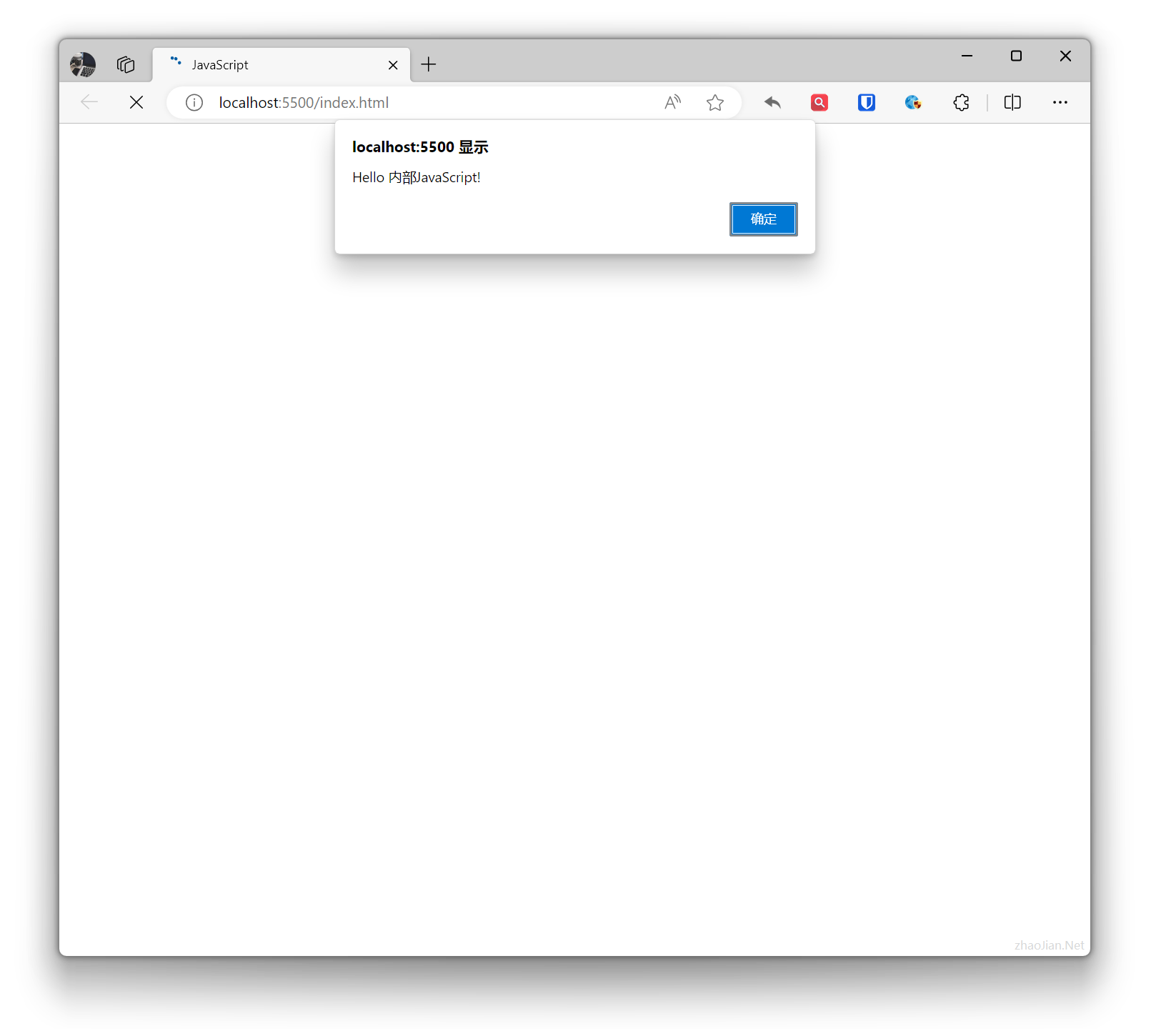
The alert dialog box is used to display a message to the user and wait for the user to click the “OK” button.
Example:
alert('Hello Internal JavaScript!');Effect:
confirm Dialog Box
The confirm dialog box is used to display a dialog box with confirm and cancel buttons to the user, typically used to ask whether the user wants to perform an operation.
Example:
let yesNo = confirm("Are you learning JavaScript?"); alert(yesNo);Effect:

prompt Dialog Box
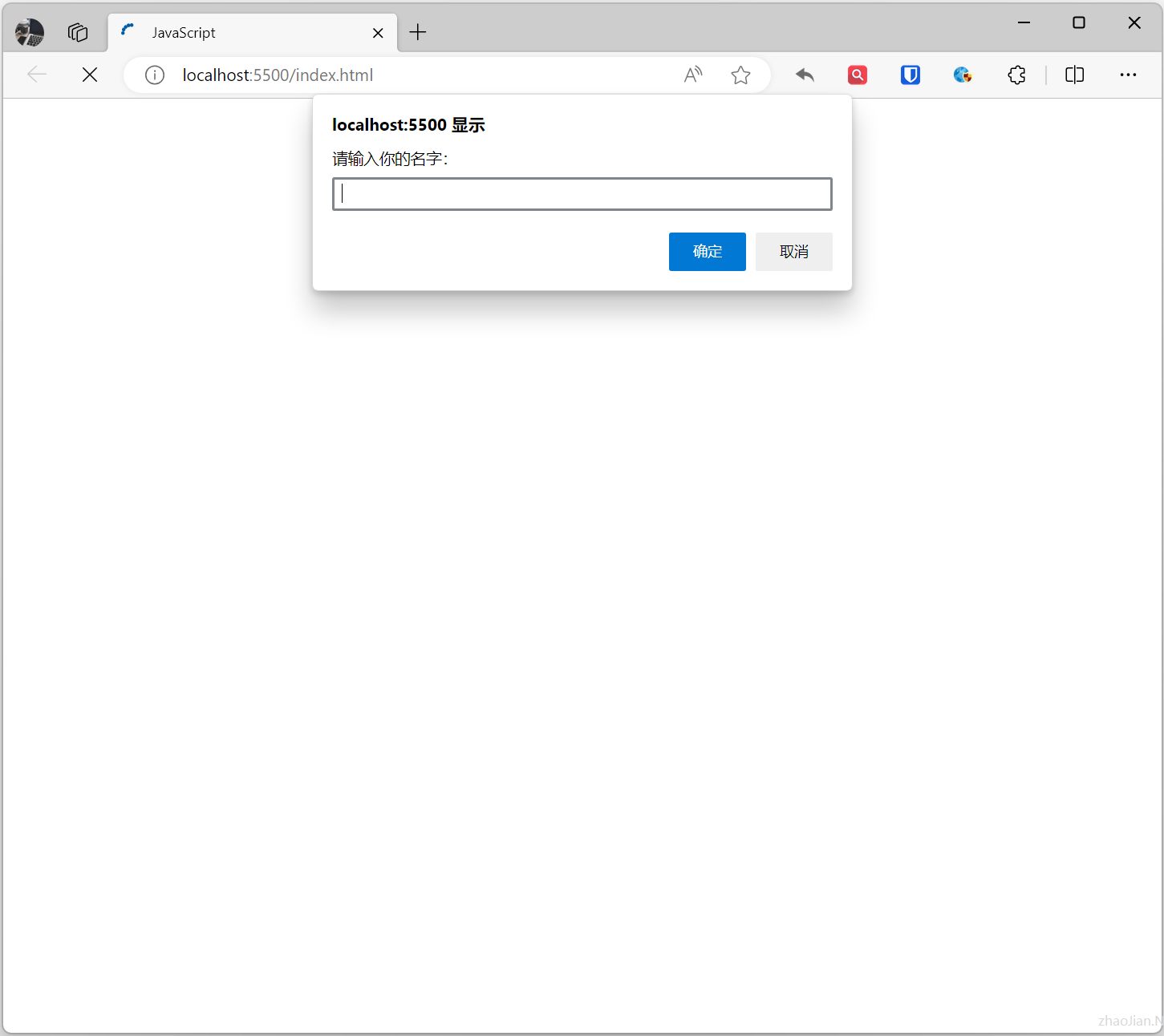
The prompt dialog box is used to display a dialog box with an input field to the user, typically used to accept user input.
Example:
let name = prompt("Please enter your name:", ''); alert(name);Effect:
Developer Tools
JavaScript developer tools are a set of tools built into browsers to help developers debug, analyze, and optimize JavaScript code. Different browsers provide different developer tools. Here are the JavaScript developer tools for common browsers:
Chrome Developer Tools
Open Chrome browser and press Ctrl + Shift + I (Windows/Linux) or Cmd + Option + I (Mac) to open Chrome Developer Tools.
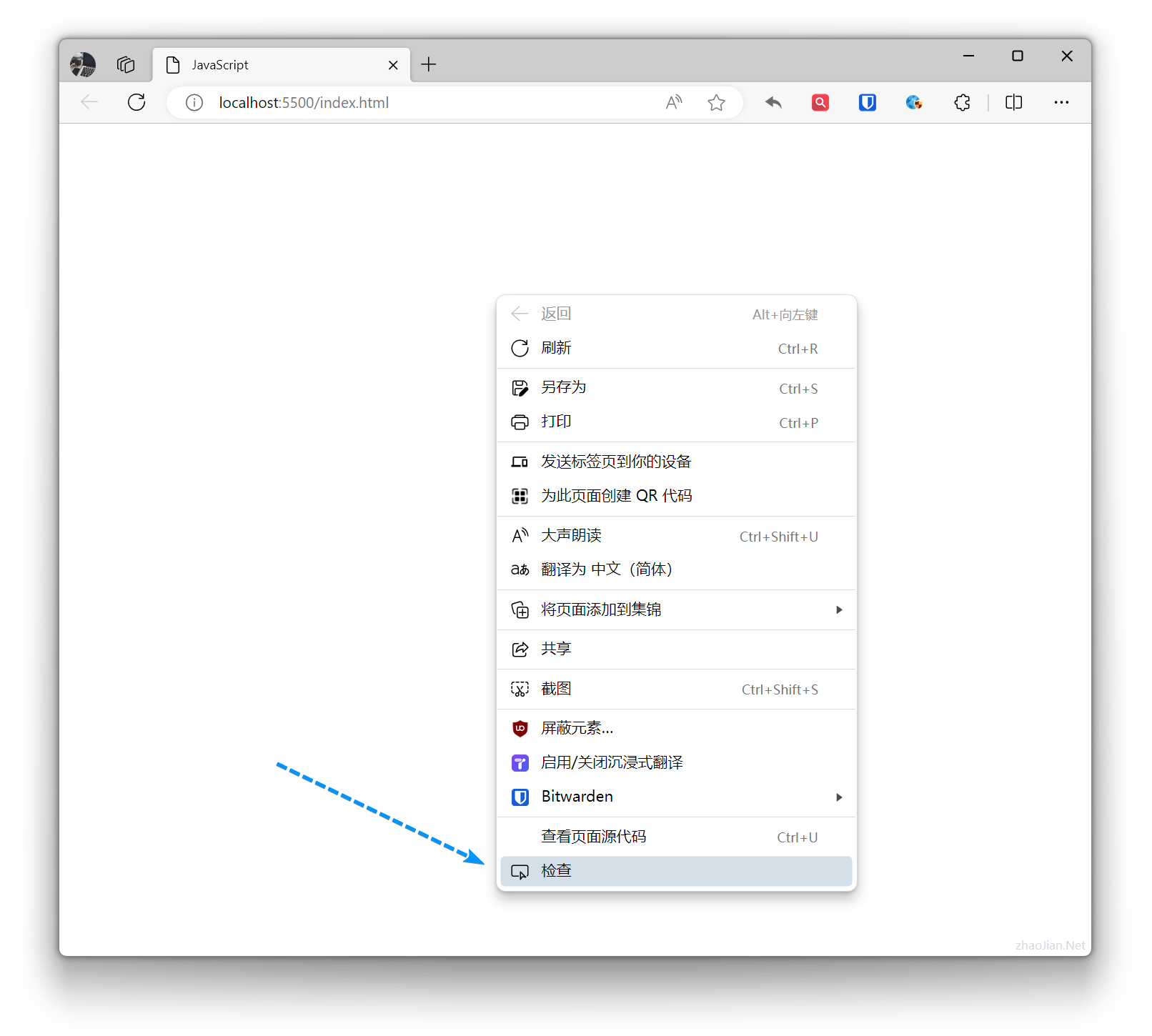
Right-click in the browser and select “Inspect” from the popup menu to open Chrome Developer Tools.
As shown:
Click the browser’s “Settings and more” icon, select “More tools” — “Developer tools” to open Chrome Developer Tools.
As shown:

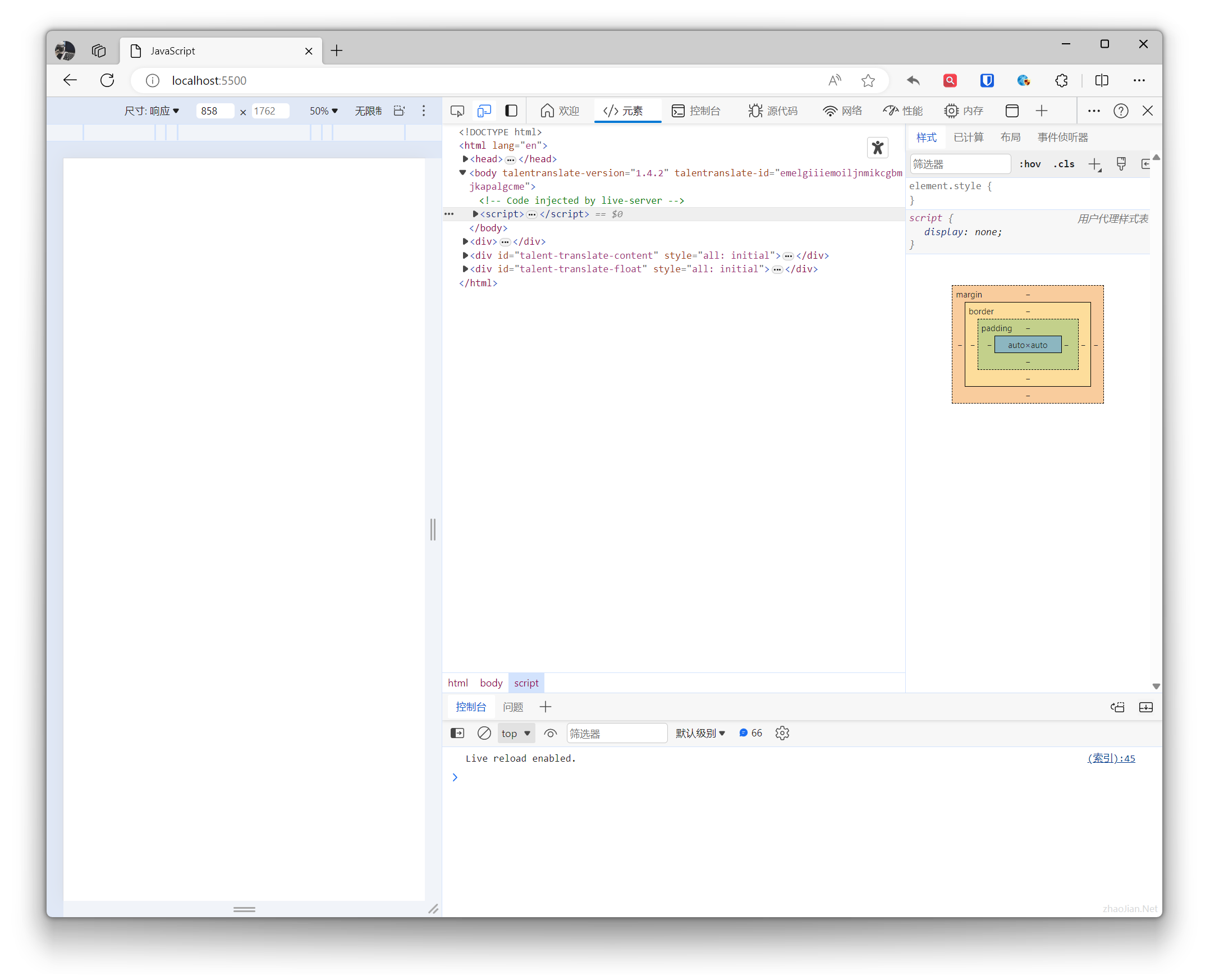
Main features and panels:
- Console: Used to execute and debug JavaScript code, view output, errors, and warning messages.
- Sources: Provides code editor, breakpoint settings, watch expressions, and other features for debugging JavaScript source code.
- Network: View network requests made by the page, inspect detailed information about requests and responses.
- Performance: Analyze page performance, view loading times, CPU usage, etc.
- Application: View and debug local storage, Session Storage, Cookies, etc.
- Elements: View and edit the DOM tree, modify CSS styles.
Keywords
JavaScript keywords are reserved words with special purposes in the JavaScript programming language. They are used to identify variables, functions, statements, etc. These keywords cannot be used as identifiers (such as variable names, function names, etc.).
Here are some JavaScript keywords:
- Basic keywords:
breakcasecatchcontinuedebuggerdefaultdeletedoelsefalsefinallyforfunctionifininstanceofnewnullreturnswitchthisthrowtruetrytypeofundefinedvarvoidwhilewith
- Reserved keywords (have special purposes in strict mode):
implementsinterfacepackageprivateprotectedpublicstaticyield
- Keywords introduced by ECMAScript 6 (ES6):
classconstexportextendsimportsuper