IT Course HTML Basics 009_Hello HTML
What is HTML?
The network, or more specifically, the World Wide Web, is composed of many linked documents and resources. These documents and resources are written in HTML, and they are called web pages. HTML is the foundation of web pages, defining their structure and content.
When you enter a web address (for example, www.zhaojian.net) in your browser, the browser sends a request to the server that provides that web page. The server responds to this request and sends the requested web page (which is some HTML) back to the browser. Then, the browser parses this HTML and displays it as the web page you typically see.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to create and design the structure of web pages. HTML consists of a series of elements, which can be used to enclose different parts of content to make them appear or work in certain ways. A pair of tags can add hyperlinks to text or images, set text to italic, bold, paragraphs, lists, etc.
[!Summary]
- HTML is not a programming language, but a markup language
- HTML documents contain HTML tags and text content (why no images)
- HTML documents are also called web pages
A Complete HTML Element
Example:
<p>hello HTML!</p>Effect:

Structure Analysis:

[!Summary]
- A complete HTML element consists of three parts: opening tag, content, and closing tag;
- Opening tag: Contains the element name (in this case, p), enclosed by left and right angle brackets. The opening tag marks where the element begins or starts to take effect;
- Content: The content of the element;
- Closing tag: Similar to the opening tag, but includes a forward slash before the element name. This marks the end of the element. Not including a closing tag is a common beginner mistake that can produce strange results.
A Complete HTML Page
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>hello HTML</title></head><body> <p>hello HTML!</p></body></html>Effect:

Structure Analysis:
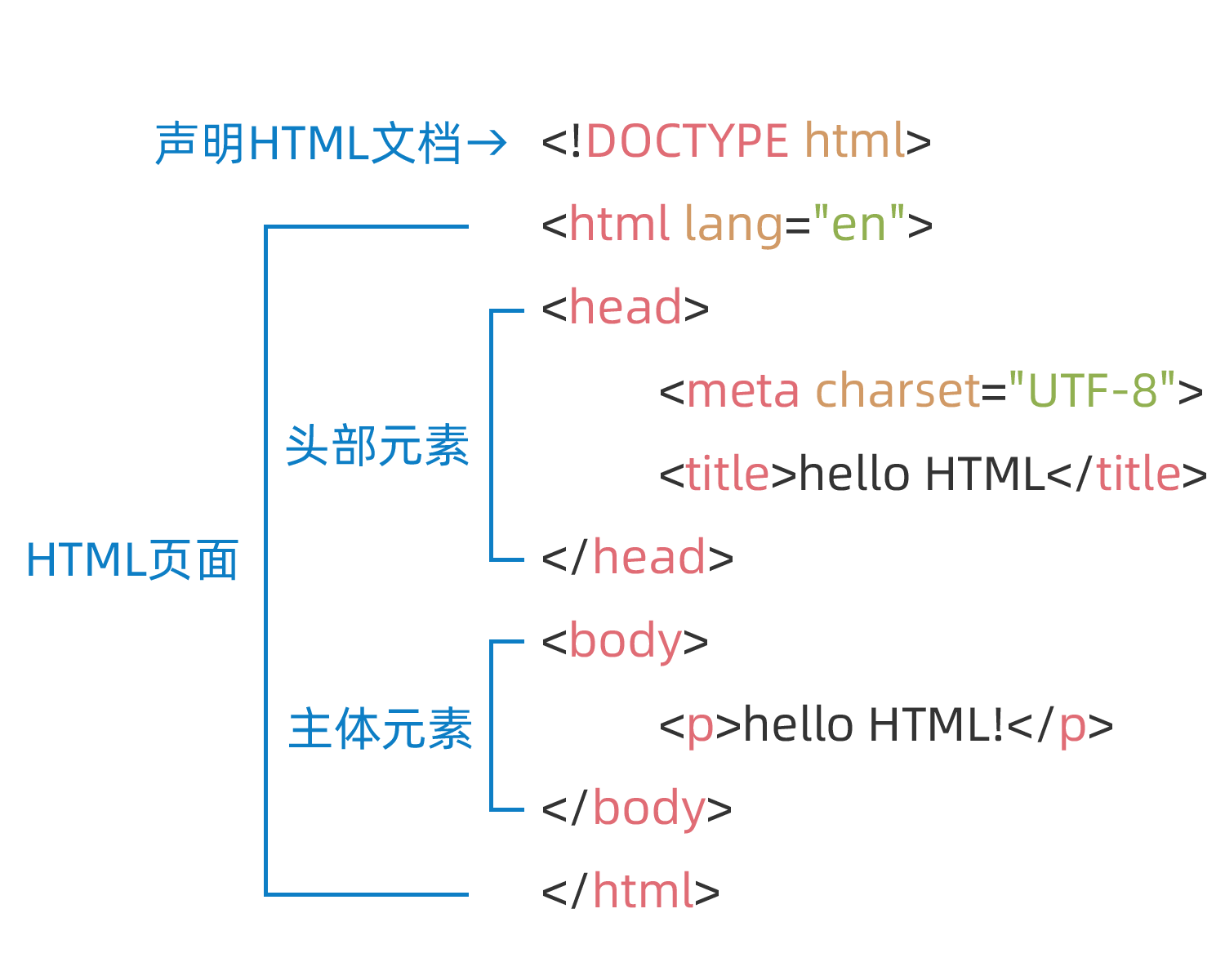
[!Summary]
<!DOCTYPE html>— Declares the HTML document type. The document type is a historical artifact used to tell the browser the version and type of the document. HTML4 strict mode DOCTYPE declaration:<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd"><html></html>— Thehtmlelement, all content in an HTML page, sometimes called the root element.<head></head>— Theheadelement, its content is not visible to users, and contains things like search keywords for search engines, page descriptions, CSS styles, JavaScript files, and character encoding declarations.<meta charset="utf-8">— Themetaelement, used to provide metadata about the HTML document. The charset attribute sets your document’s character set to UTF-8.<title></title>— Thetitleelement. This element sets the page title, which is displayed on the browser tab and used as the description text when bookmarking the page.<body></body>— Thebodyelement. This element contains the content you want users to see when they visit the page, including text, images, videos, games, playable audio tracks, or other content.<p></p>— The paragraph element, representing a paragraph of text.
Element Name | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
<!DOCTYPE html> | Defines the type and version of the HTML document | <!DOCTYPE html> |
<html> | Defines the root element of the HTML document | <html lang="en"> |
<head> | Contains meta-information about the document, such as title, character set declaration, style and script links, etc. | <head>...</head> |
<title> | Defines the title of the document, displayed in the browser’s title bar or tab | <title>My Web Page</title> |
<meta> | Provides meta-information about the document, such as character set, viewport settings, keywords, etc. | <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> |
<link> | References external resources, such as stylesheets and icons | <link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css"> <link rel="icon" href="favicon.ico" type="image/x-icon"> |
<style> | Internally defines the document’s styles | <style>body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; }</style> |
<script> | Defines or references scripts, can be included in the document or reference external scripts | <script src="script.js"></script> |
<noscript> | Defines content to display when the browser doesn’t support scripts | <noscript>Sorry, your browser does not support JavaScript.</noscript> |
<base> | Specifies the base URL for all relative links in the page | <base href="https://www.zhaojian.net/"> |
Links:
VS Code Extensions: Remote - SSH Remote Development