IT Course CSS Basics 028_Float, Positioning, Alignment
Float
In CSS, float is a layout technique that uses the float property to make elements float along the left or right side of the container, allowing other elements to wrap around it.
Example:
.div-left { float: left; } .div-right { float: right; } <div class="div-left">div-left</div> <div class="div-right">div-right</div>Effect:
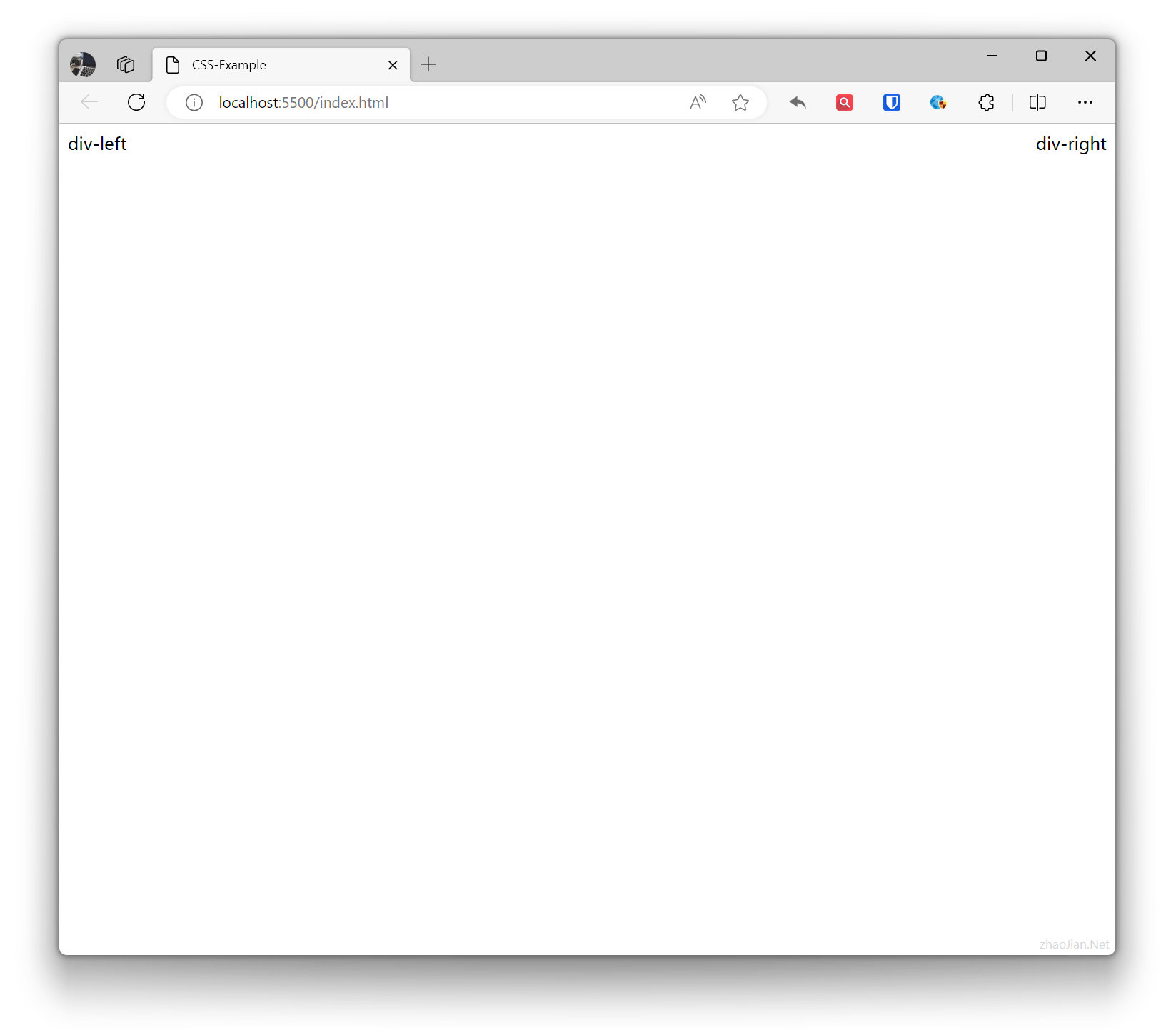 Floating elements may cause the parent element’s height to collapse, may affect elements in other DIVs, and multiple floating elements on the same line may overlap. The
Floating elements may cause the parent element’s height to collapse, may affect elements in other DIVs, and multiple floating elements on the same line may overlap. The clear property is needed to control their mutual effects.
Example:
.div-left { float: left; } .div-right { float: right; } /* Use `clear` property to cancel floating element effects .content { clear: both; } */ <div class="div-left">div-left</div> <div class="div-right">div-right</div>
<div class="content"> This is text that will be affected. </div>Effect:
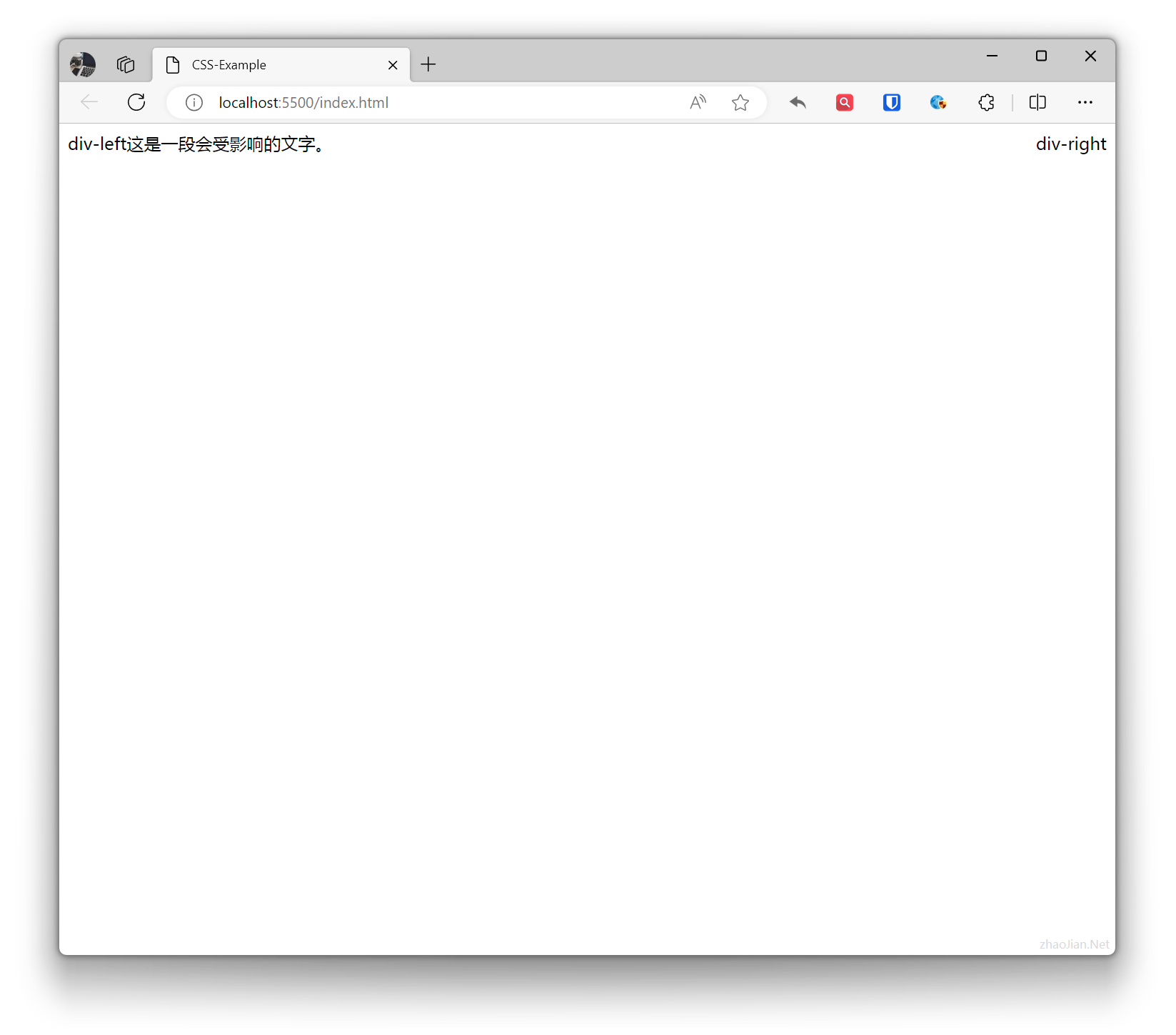 Example:
Example:
.float-left { float: left; } .float-right { float: right; } <img class="float-left" src="zhaojian1.jpg" alt="" srcset=""> <div class="float-right">January 25, 2024</div><div class="float-right">Article Title Article Title Article Title</div>Effect:
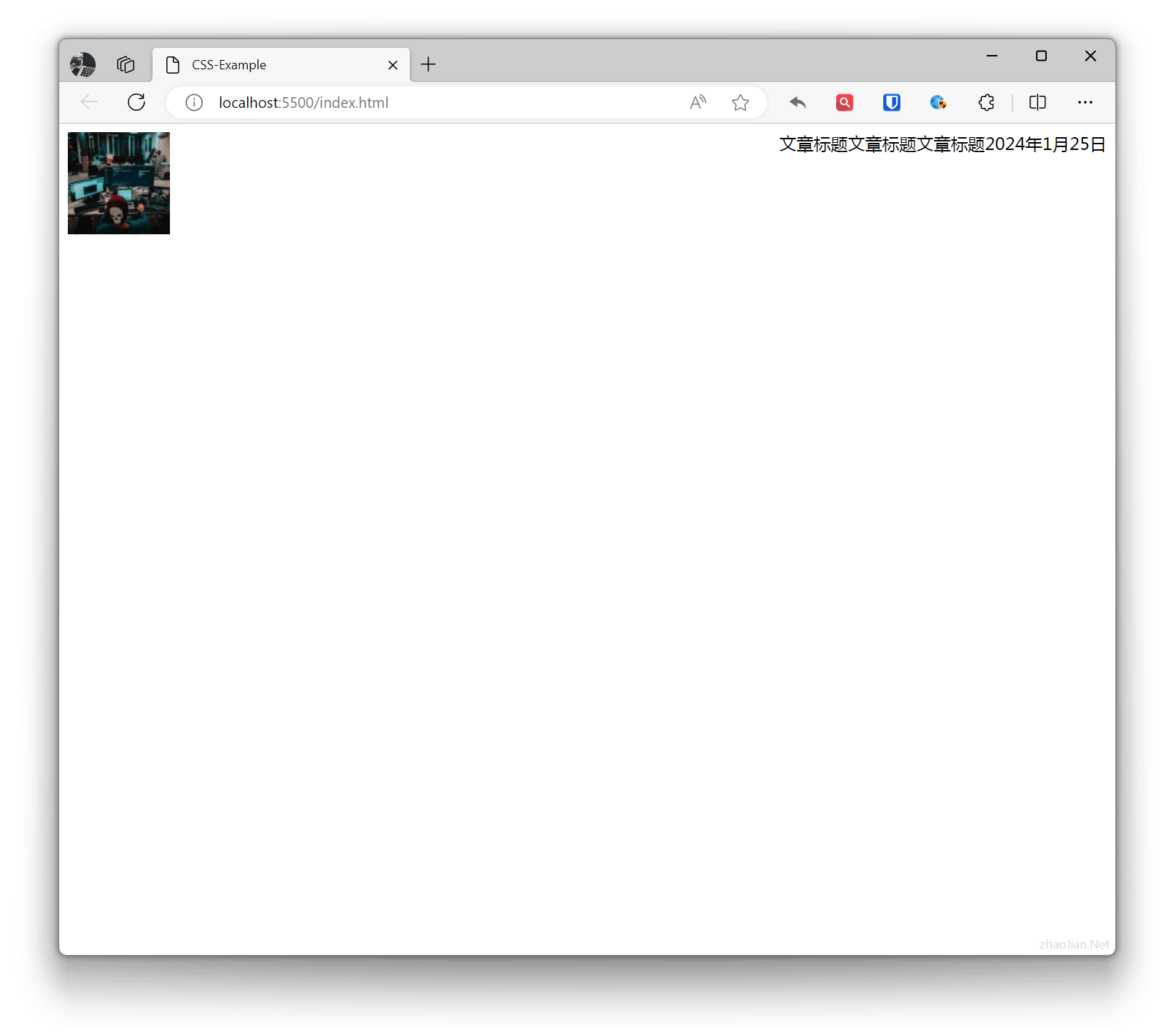
Float was an early technique for creating multi-column layouts, but in modern layouts, more flexible layout techniques like Flexbox or Grid are usually recommended.
Positioning
In CSS, positioning refers to setting the positioning method of elements through the position property, and specifying the position of elements relative to their nearest positioned parent elements through the top, right, bottom, left properties.
- Positioning is relative to the nearest positioned (position is not
static) ancestor element. If there is no positioned ancestor element, it is positioned relative to the initial containing block (usually the<html>element). - Absolutely positioned and fixed positioned elements are removed from the normal document flow and may affect the layout of other elements.
- Property values typically use pixels (
px) or percentages (%).
Static Positioning static
Static Positioning is the default value of the position property and usually does not need to be explicitly specified. Statically positioned elements are arranged normally in the document flow and are not affected by the top, right, bottom, left properties.
Initial Positioning initial
In CSS, initial is a keyword used to reset property values to their initial values. For the position property, its initial value is static. Using position: initial; is equivalent to not setting the position property.
Relative Positioning relative
The element is positioned relative to its normal position.
Example:
.base { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: aquamarine; } .relative-example { position: relative; top: 100px; left: 20%; } <!-- <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br> Try adding br or other elements --> <div class="base relative-example"></div>Effect:
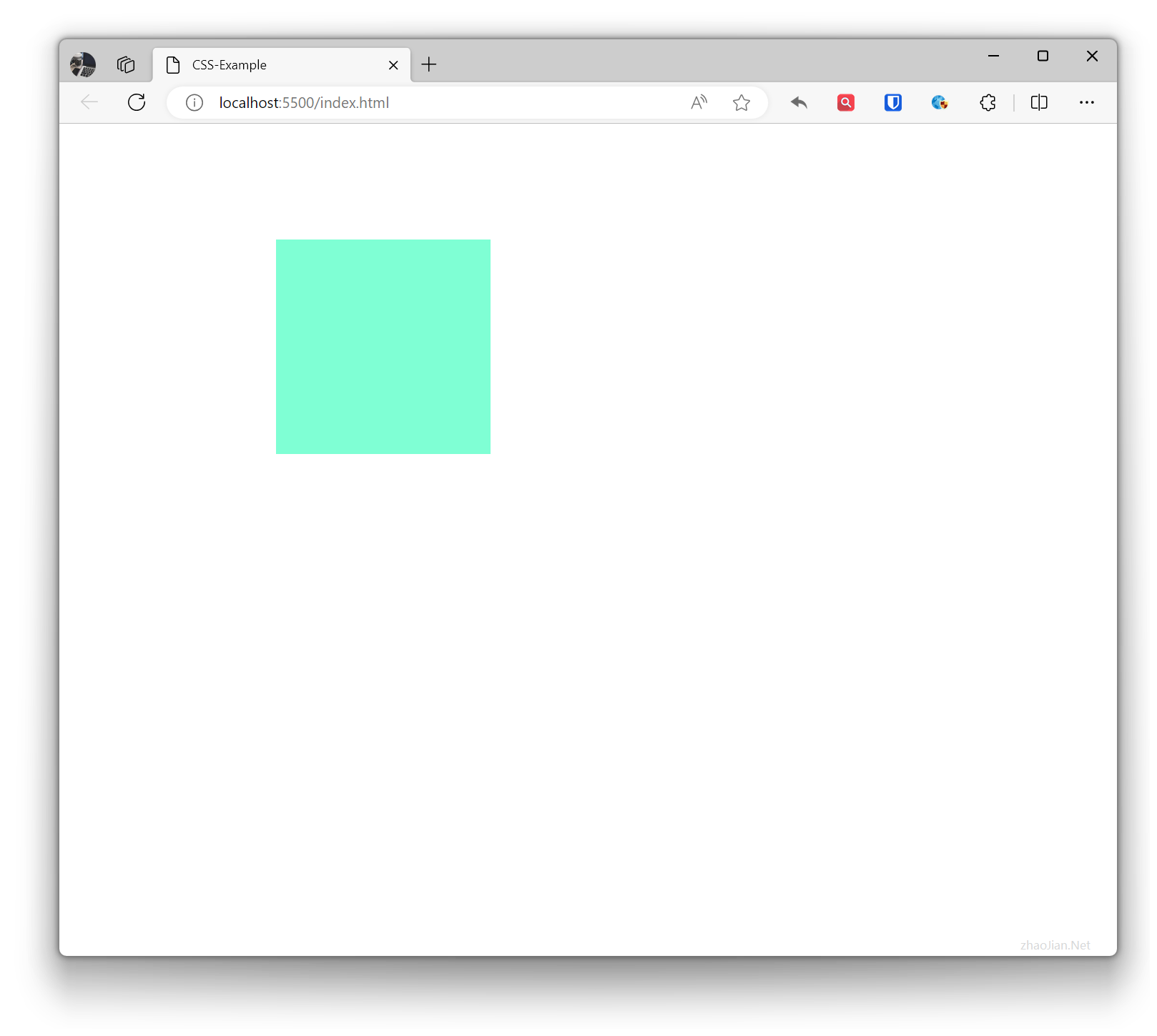
Absolute Positioning absolute
The element is positioned relative to its nearest positioned ancestor element.
Example:
.base { width: 200px; height: 200px; } .absolute-example { position: absolute; top: 50px; left: 100px; background-color: blueviolet; } <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br> <div class="base absolute-example"></div>Effect:
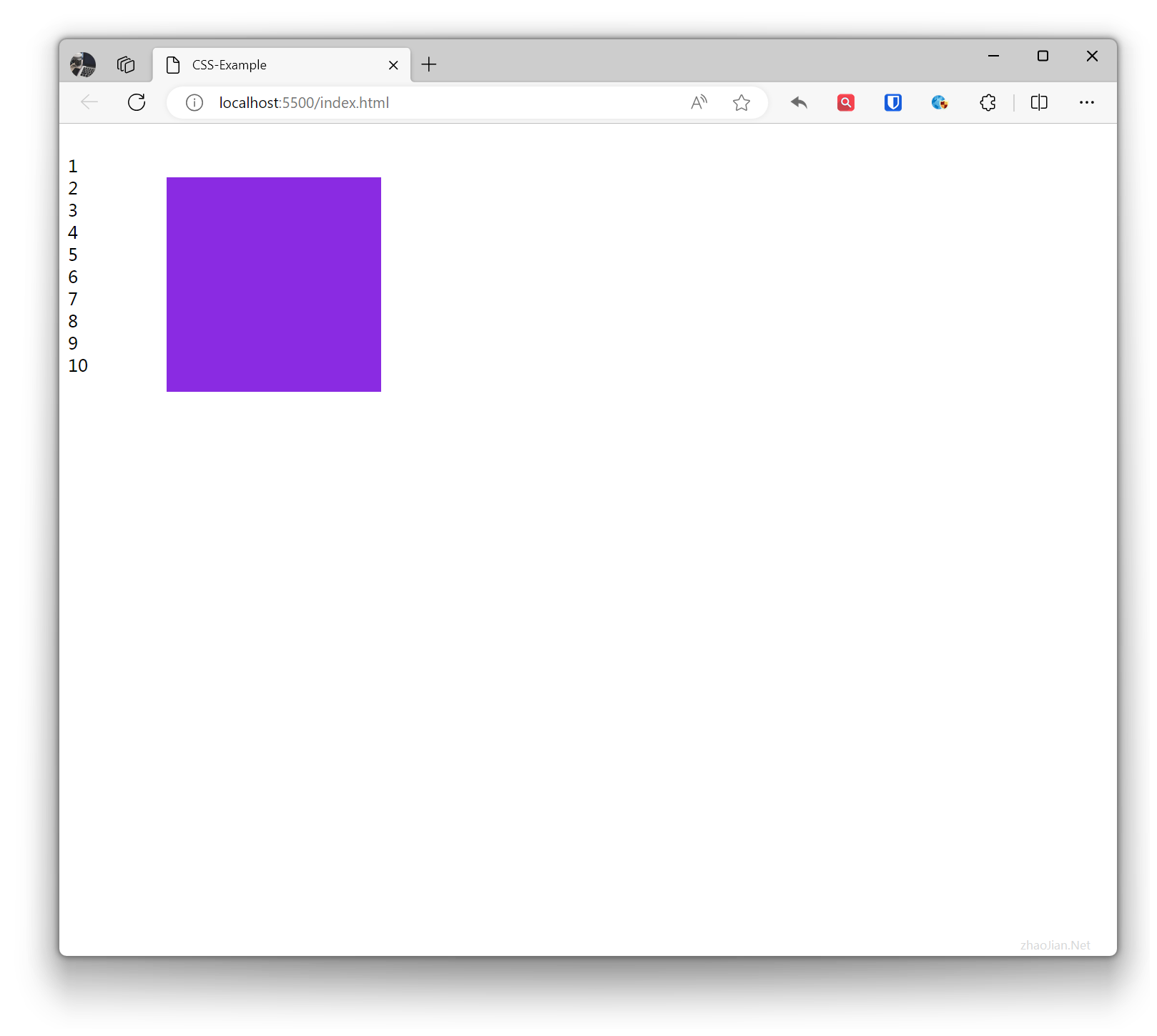
Fixed Positioning fixed
The element is positioned relative to the browser window and always maintains a fixed position on the screen.
Example:
.base { width: 200px; height: 200px; } .fixed-example { position: fixed; bottom: 40%; left: 40%; background-color: gold; } <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br> <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br> <div class="base fixed-example"></div> <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br> <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br>Effect:
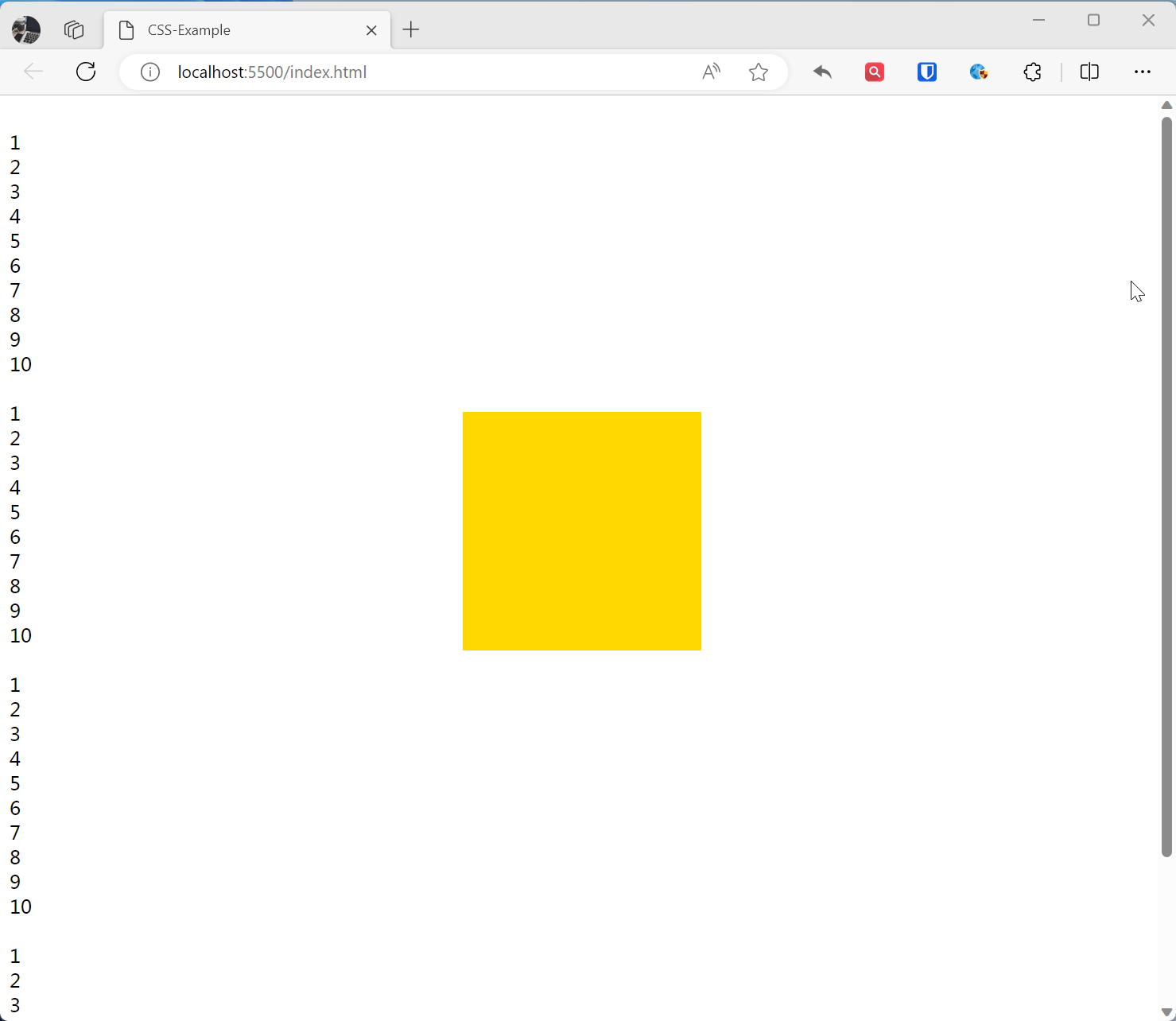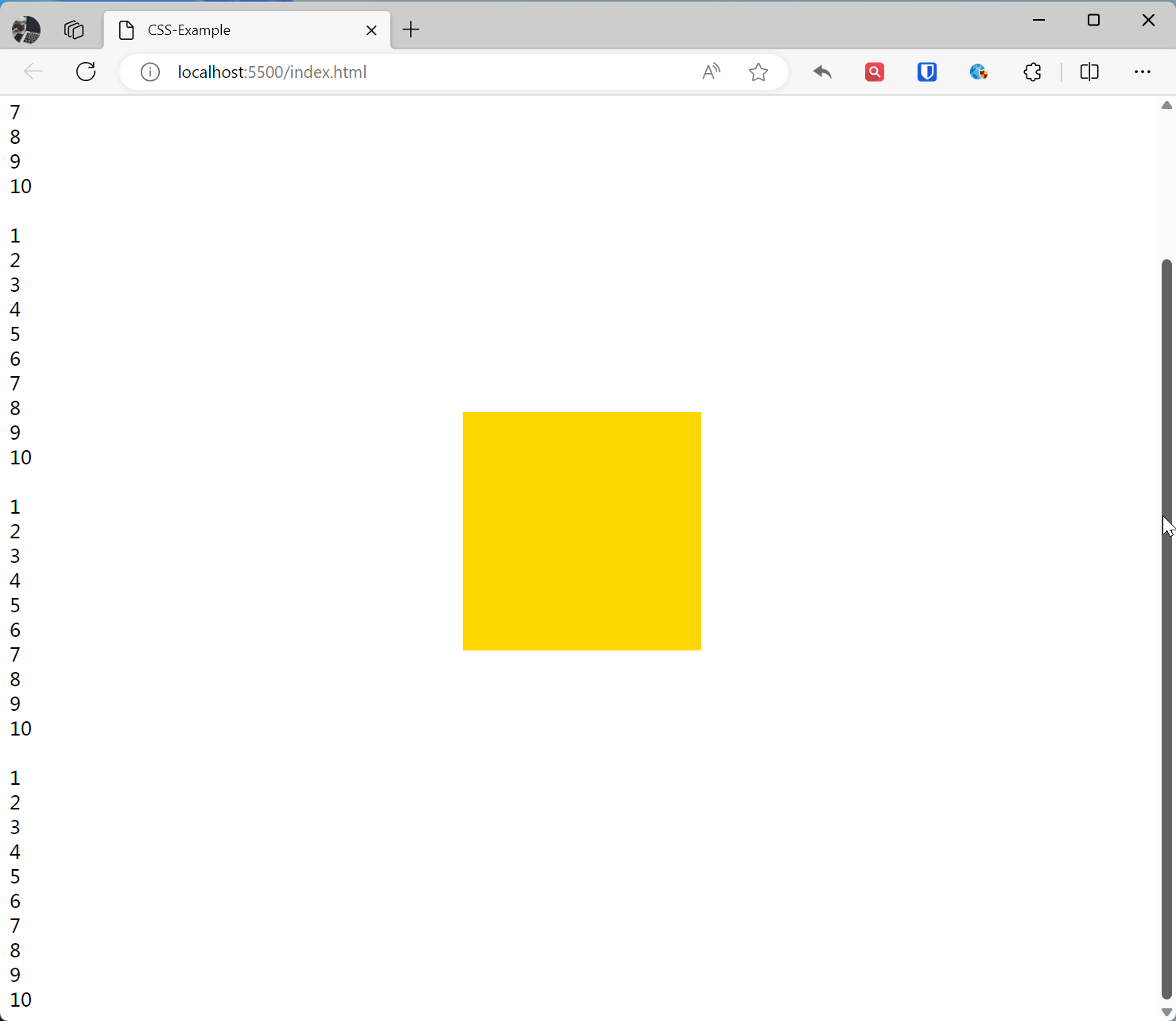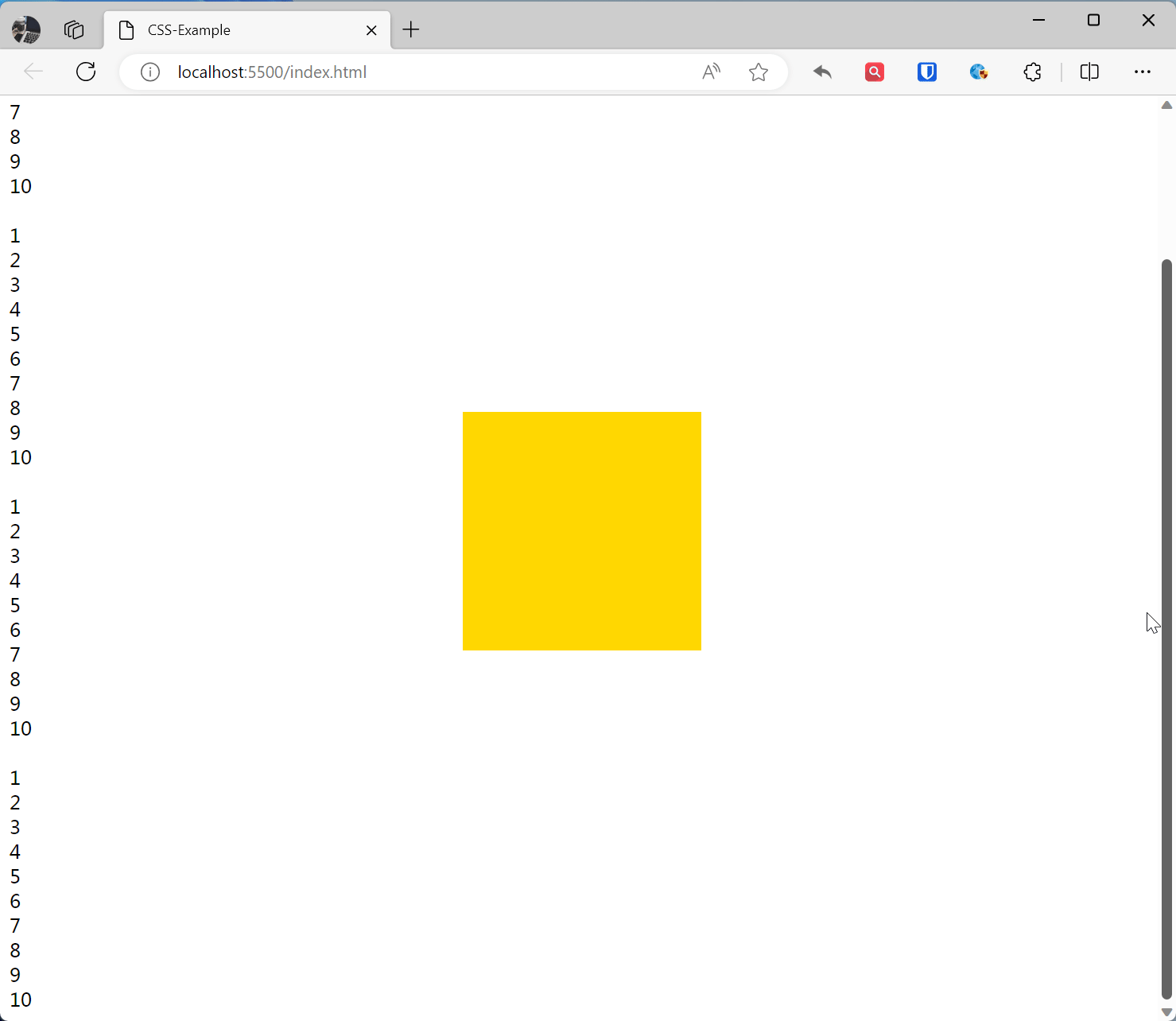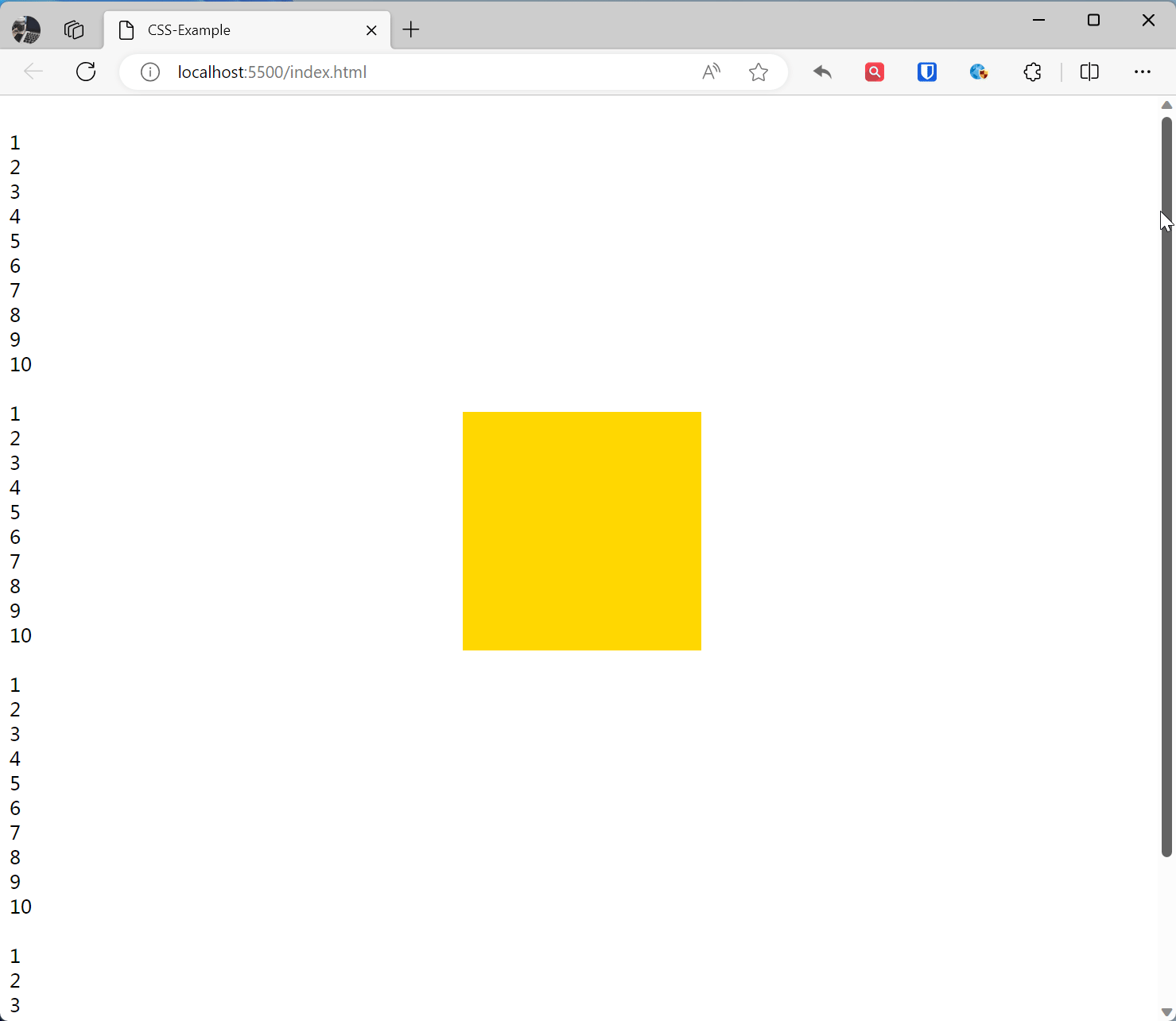
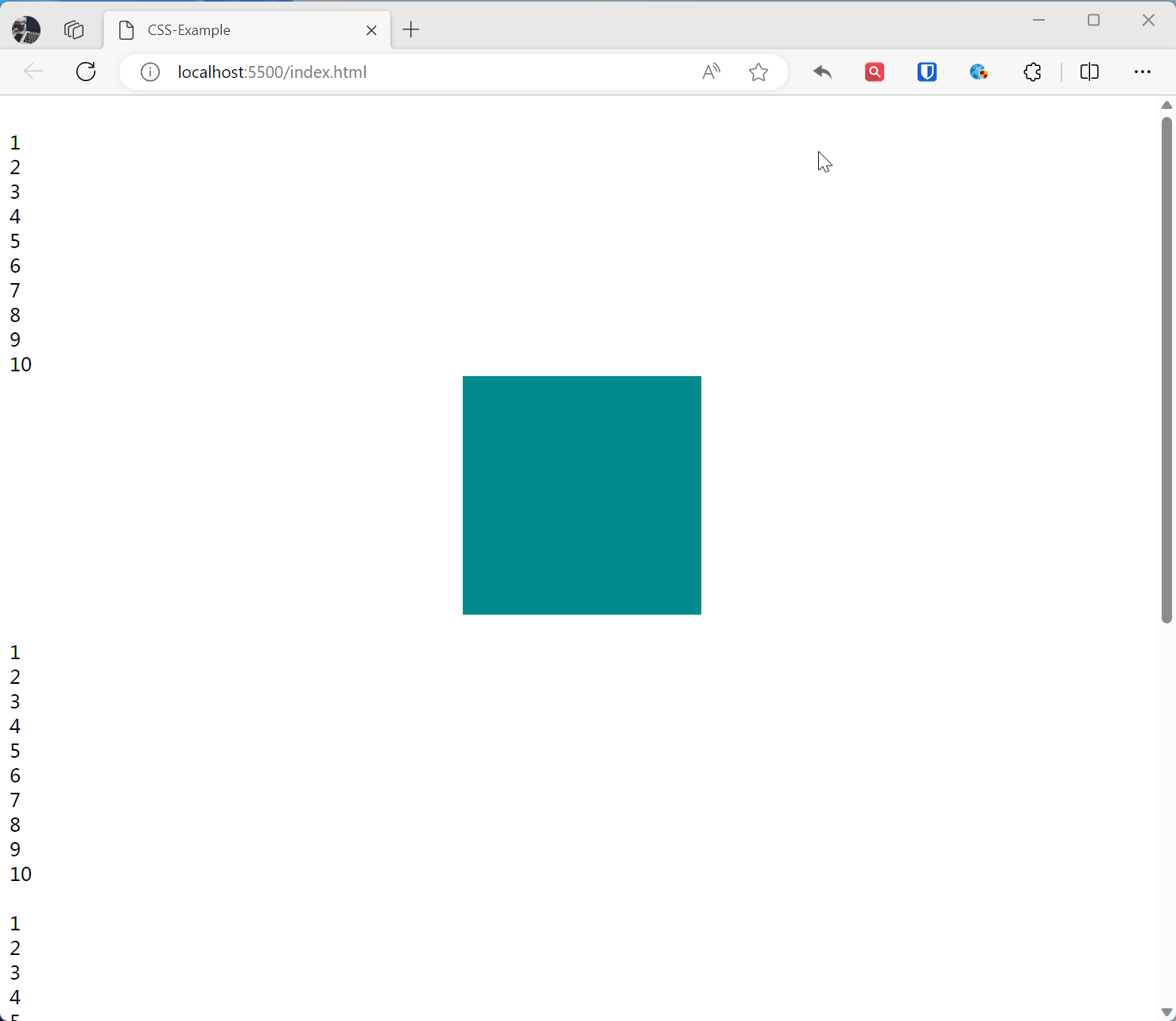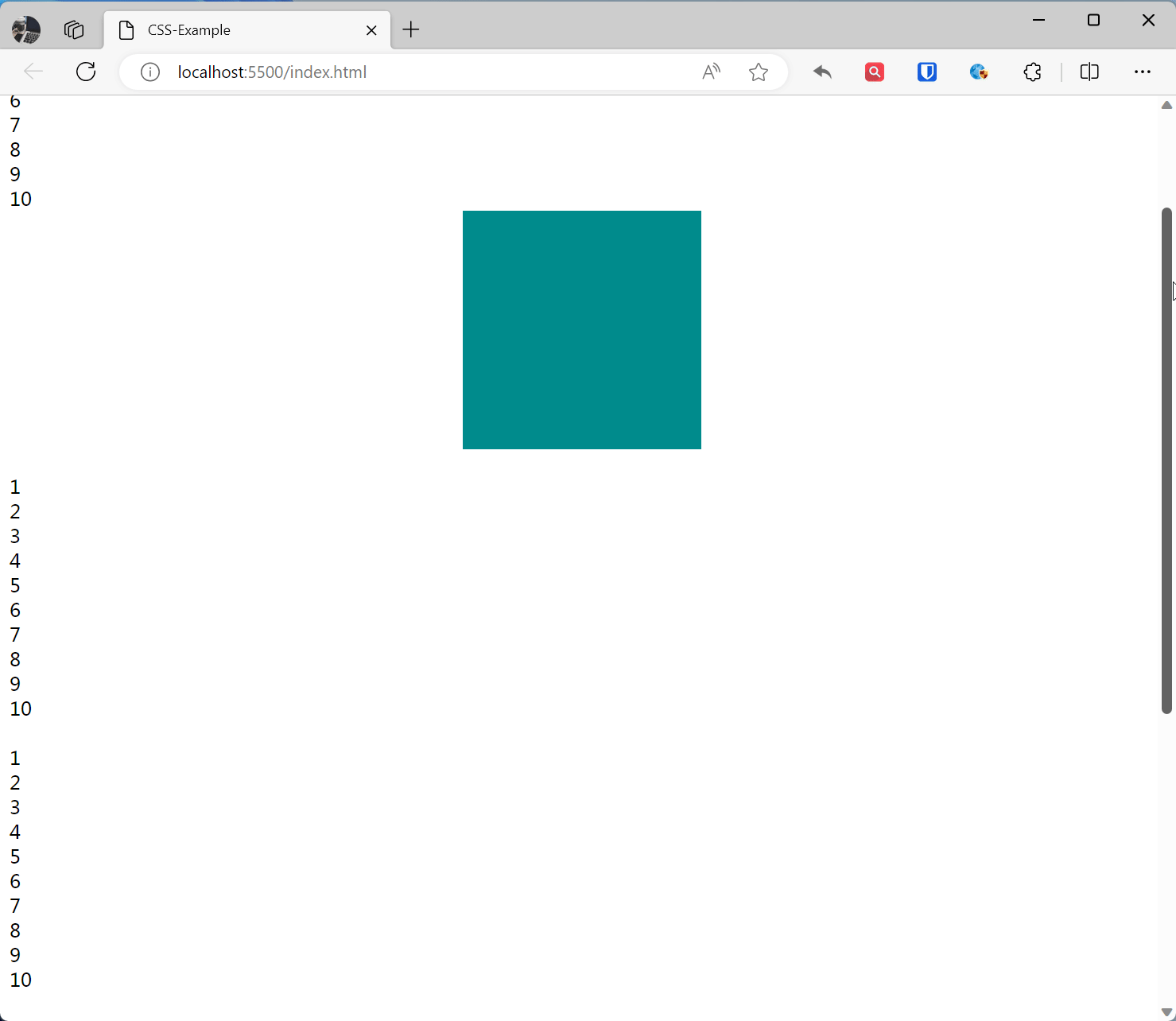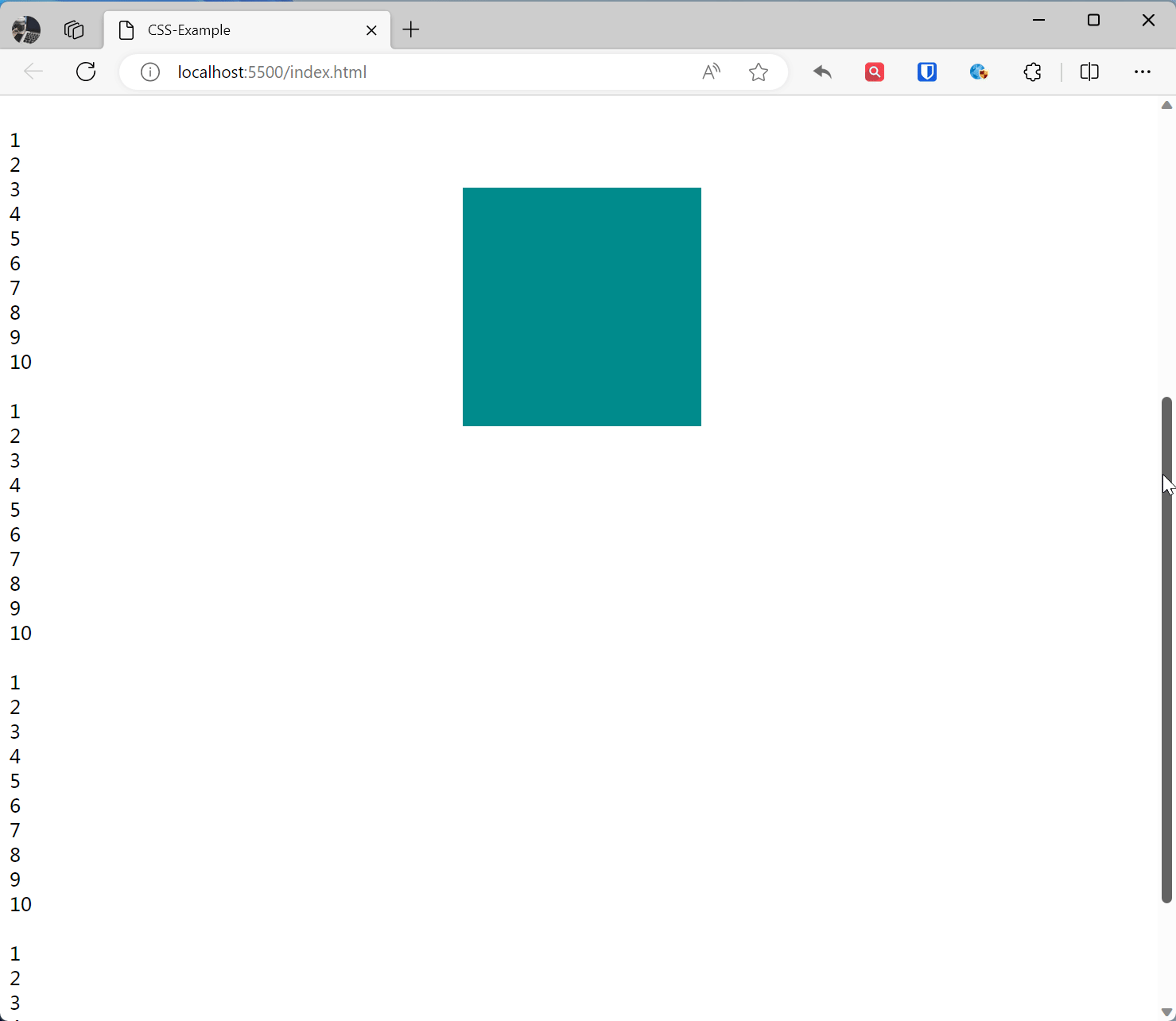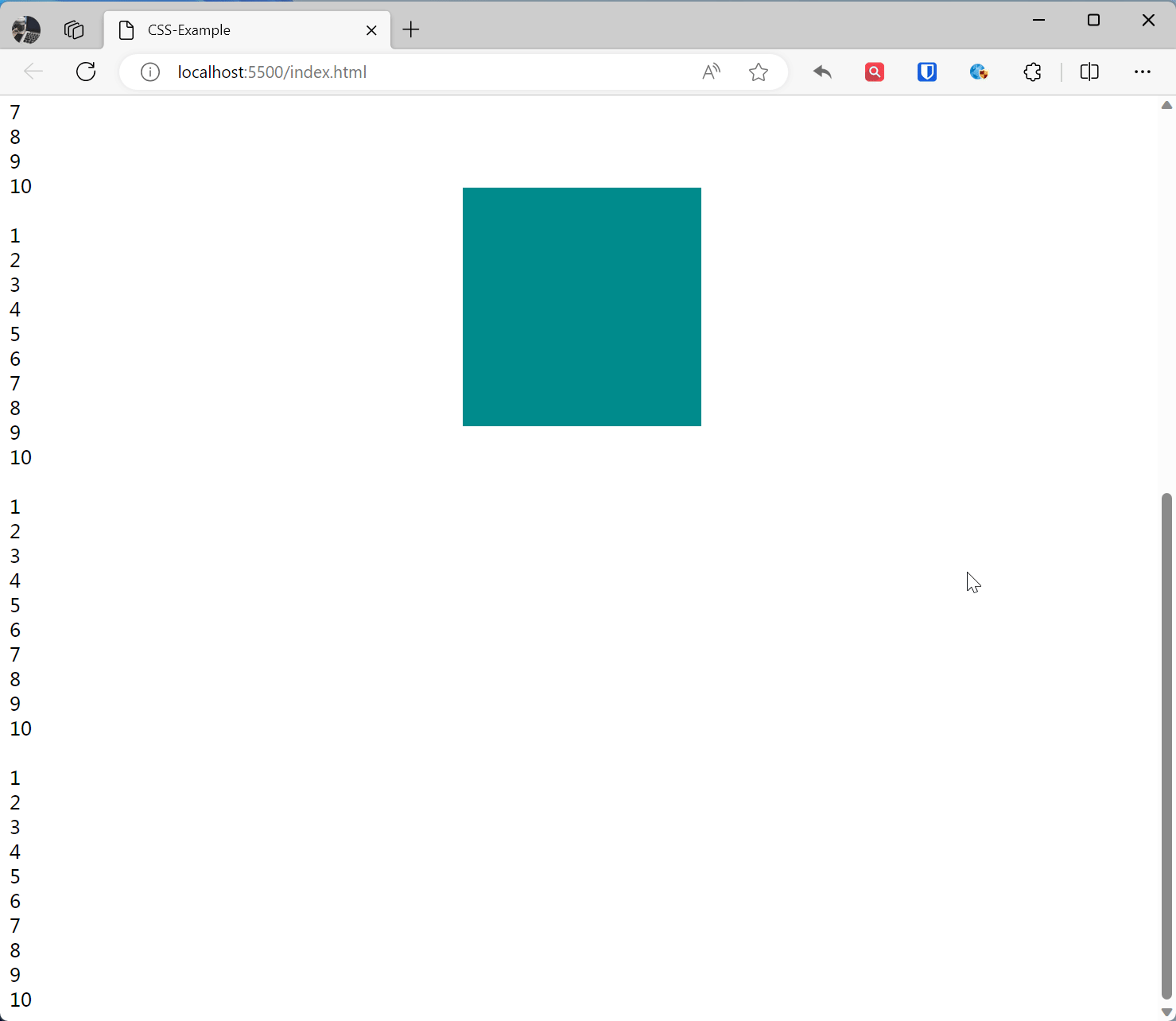
Sticky Positioning sticky
The element becomes fixed positioned when scrolled to a specific position, otherwise it is relatively positioned.
Example:
.base { width: 200px; height: 200px; } .sticky-example { position: sticky; top: 10%; left: 40%; background-color: darkcyan; } <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br> <div class="base sticky-example"></div> <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br> <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br> <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br> <br>1<br>2<br>3<br>4<br>5<br>6<br>7<br>8<br>9<br>10<br>Effect:
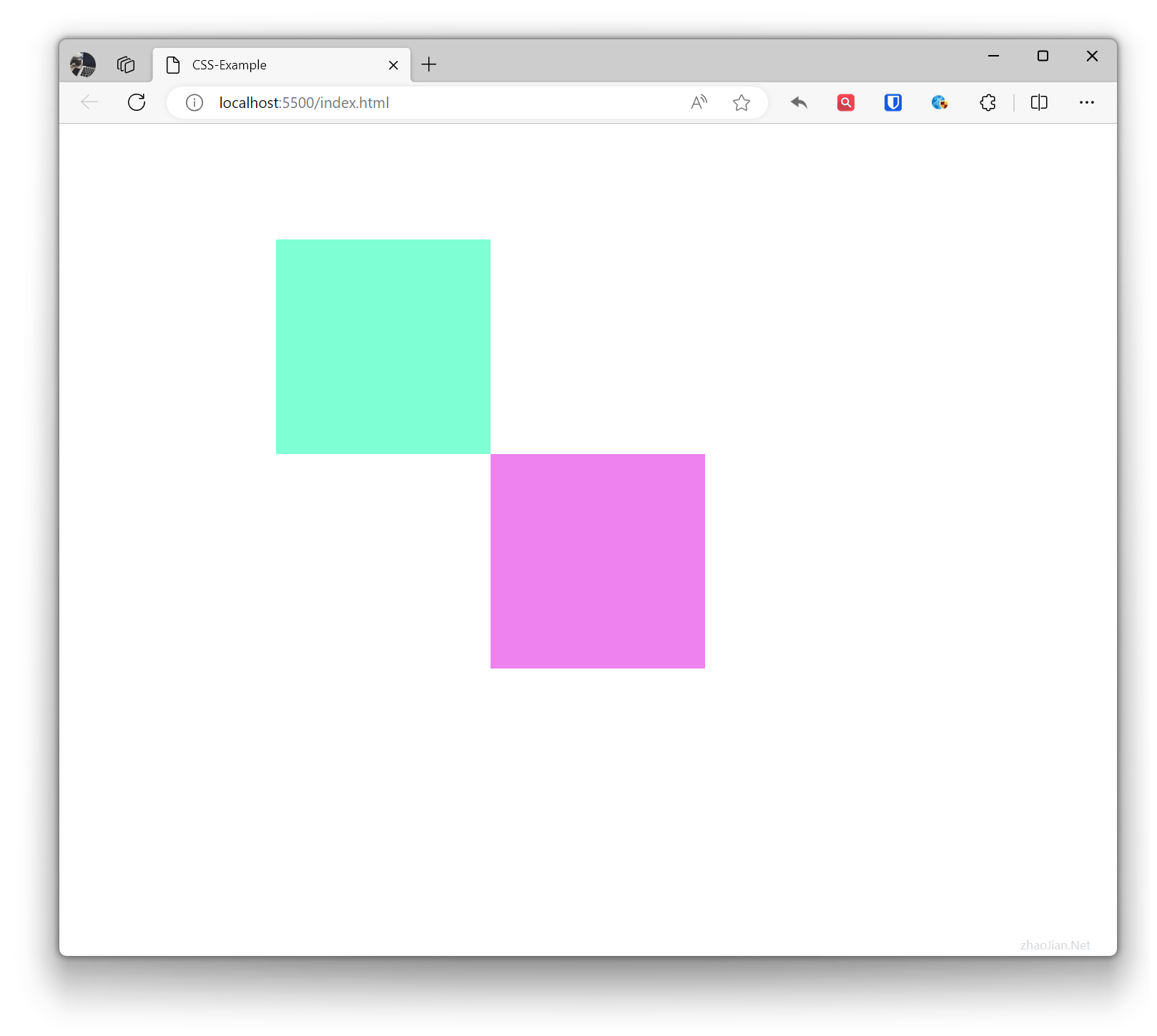
Inherit Positioning inherit
The element becomes fixed positioned when scrolled to a specific position, otherwise it is relatively positioned.
Example:
.base { width: 200px; height: 200px; } .inherit-example { position: inherit; top: 100%; /* Note the boundary */ left: 100%; /* Note the boundary */ background-color: violet; } <div class="base relative-example"> <div class="base inherit-example"></div> </div>Effect:
Stacking Order (Overlapping Elements)
z-index is a CSS property used to control stacking order. It determines the display order of an element in vertical stacking, i.e., which element will be in front of or behind which element.
z-indexvalues can be negative.- Elements with larger
z-indexwill cover elements with smaller values. z-indexonly works on positioned elements (positionis notstatic)z-indexrequires the element’sopacityto be set to non-0
Example:
.base { width: 200px; height: 200px; position: absolute; } .z-index-example1{ background-color: red; z-index: 9; } .z-index-example2{ background-color: blue; z-index: 1; } <div class="base z-index-example1"></div> <div class="base z-index-example2"></div>Alignment
CSS alignment refers to controlling the horizontal and vertical alignment of elements through CSS properties. CSS alignment properties can be applied to any element, including text, images, tables, lists, etc.
Common alignment properties have the following values:
- left: Left alignment
- center: Center alignment
- right: Right alignment
- top: Top alignment
- middle: Middle alignment
- bottom: Bottom alignment
Horizontal Alignment text-align
Used to set the horizontal alignment of text content in the element box.
Example:
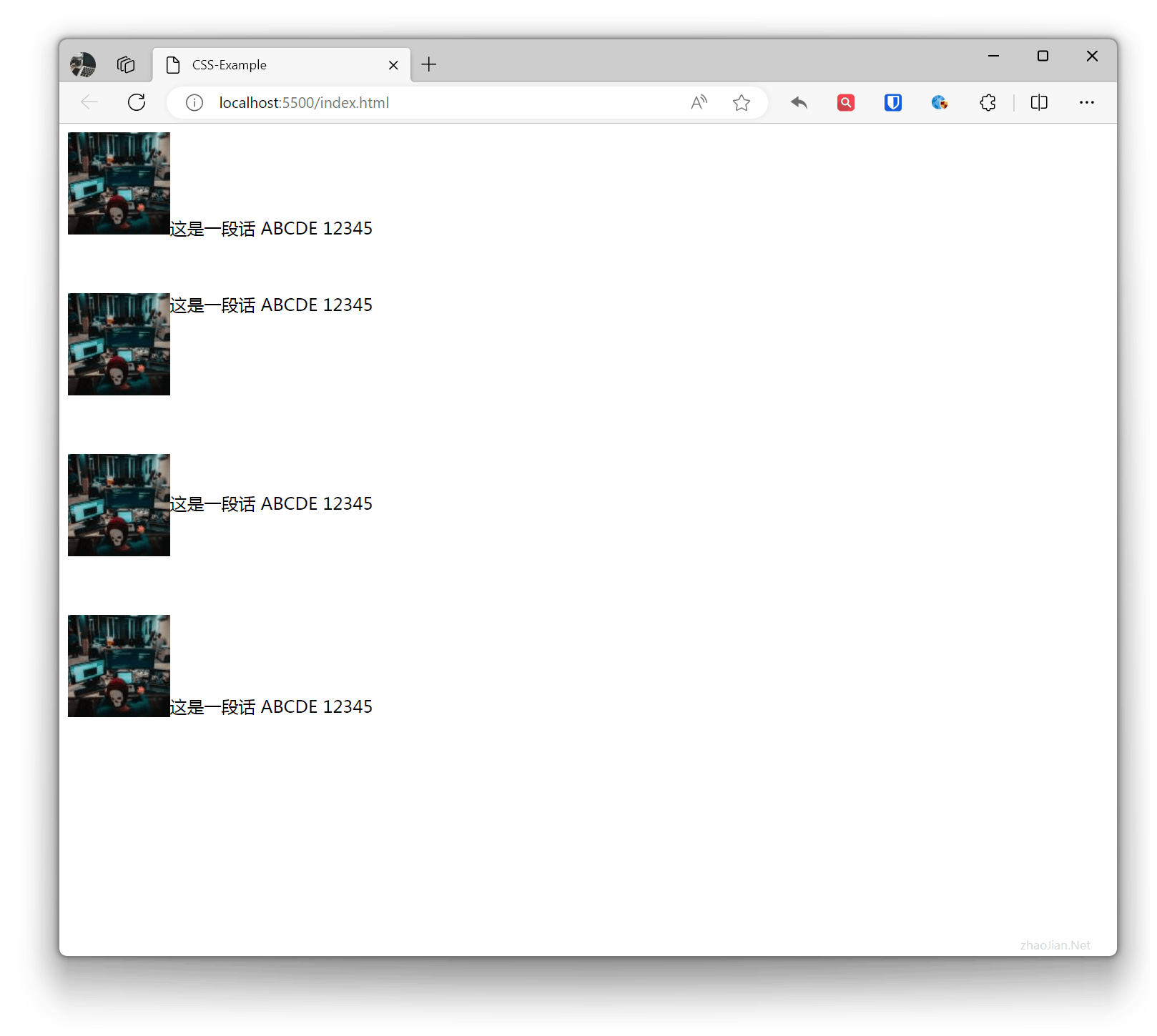
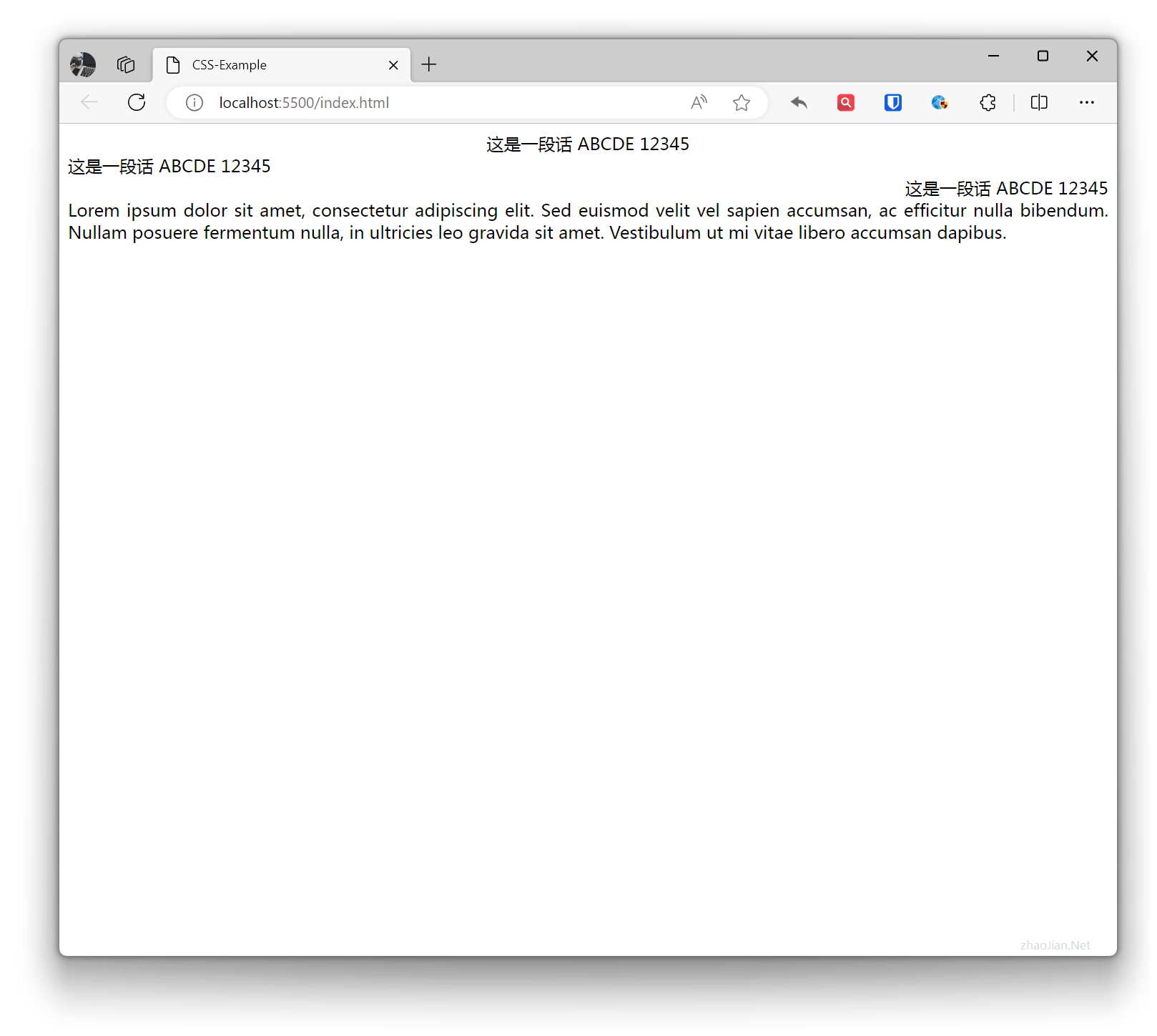
.text-center { text-align: center; /* Horizontal center alignment */}.text-left { text-align: left; /* Left alignment */}.text-right { text-align: right; /* Right alignment */}.text-justify { text-align: justify; /* Justify alignment */} <div class="text-center">This is a sentence ABCDE 12345</div> <div class="text-left">This is a sentence ABCDE 12345</div> <div class="text-right">This is a sentence ABCDE 12345</div> <div class="text-justify">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed euismod velit vel sapien accumsan, ac efficitur nulla bibendum. Nullam posuere fermentum nulla, in ultricies leo gravida sit amet. Vestibulum ut mi vitae libero accumsan dapibus.</div>Effect:
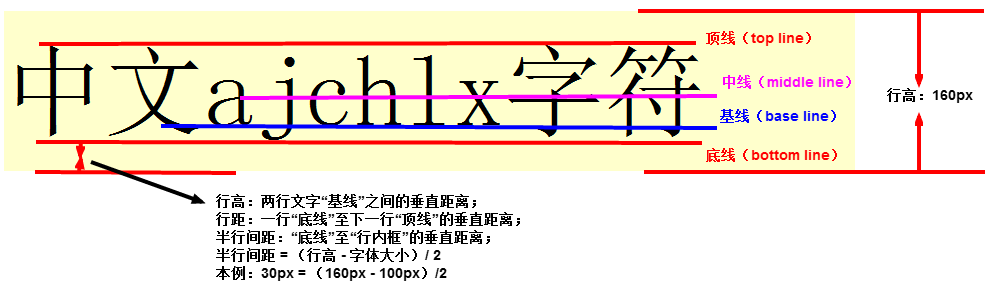
Vertical Alignment vertical-align
Used to set the vertical alignment of inline elements within an element. Usually used for inline elements and has no direct effect on block-level elements.
Example:
.base{ height: 150px;}.vertical-align-baseline { vertical-align: baseline; /* Default baseline alignment */}.vertical-align-top { vertical-align: top; /* Top alignment */}.vertical-align-middle { vertical-align: middle; /* Middle alignment */}.vertical-align-bottom { vertical-align: bottom; /* Bottom alignment */} <div class="base"> <img class="vertical-align-baseline" src="zhaojian1.jpg" alt="" srcset="">This is a sentence ABCDE 12345 </div> <div class="base"> <img class="vertical-align-top" src="zhaojian1.jpg" alt="" srcset="">This is a sentence ABCDE 12345 </div> <div class="base"> <img class="vertical-align-middle" src="zhaojian1.jpg" alt="" srcset="">This is a sentence ABCDE 12345 </div> <div class="base"> <img class="vertical-align-bottom" src="zhaojian1.jpg" alt="" srcset="">This is a sentence ABCDE 12345 </div>Effect: