IT Course CSS Basics 019_HelloCSS
What is CSS?
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), similar to HTML, is not a real programming language, or even a markup language. CSS is a style sheet language used to add styles to HTML elements, describe the appearance of HTML documents, and control the color, size, font, layout, etc. of HTML document elements.
CSS is an important part of web development that can help you create beautiful, easy-to-use web pages.
Basic Structure of CSS
CSS styles consist of selectors and properties. Selectors are used to select the HTML elements to which styles will be applied. Properties are used to specify the values of styles.
Example:
p { color: red;}Effect:
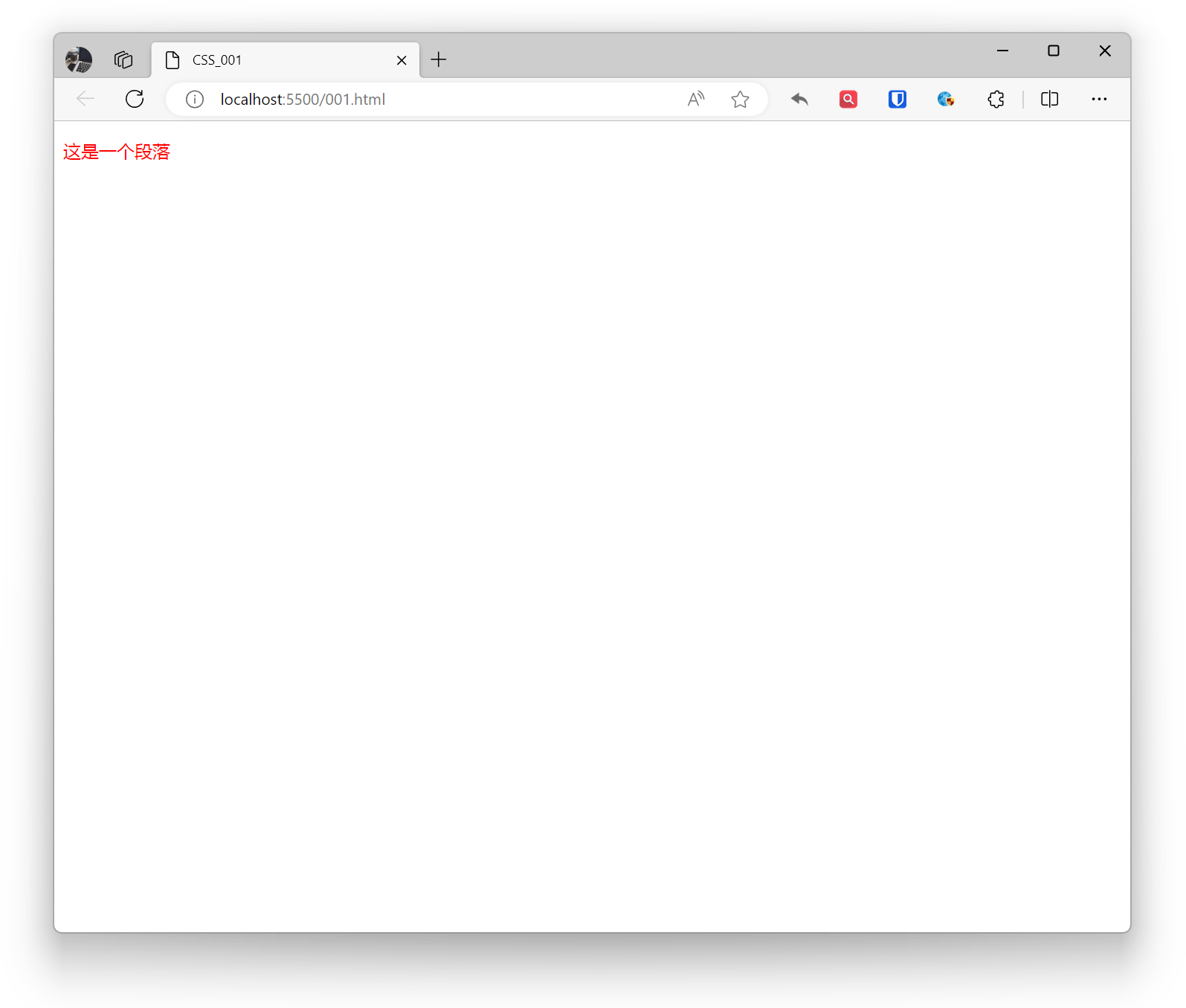
Structure Analysis:

[!Summary]
Selector The name of the HTML element is at the beginning of the rule set. It selects one or more elements that need to be styled (in this example, the
<p>element). To style different elements, simply change the selector.Declaration A single rule, like color: red; specifies the property of the element to be styled. CSS declarations always end with a semicolon ; and are always enclosed in curly braces {}:
Properties Ways to change the style of HTML elements (in this example, color is a property of the
<p>element). In CSS, the author decides which property to modify to change the rule.Property value To the right of the property, after the colon, is the property value, which selects one value from many possible appearances of the specified property (besides red, we have many other property values for color).
How to Reference CSS?
Inline Reference:
Write CSS code directly in HTML tags using the style attribute.
Inline reference is a simple and quick method of writing style code directly in HTML tags. The advantage of inline reference is convenience and speed, suitable for small amounts of styles. However, inline reference also has the following disadvantages:
- Not conducive to style reuse, difficult to maintain.
- HTML files become messy, not in accordance with separation principles.
- Not conducive to browser caching, affecting performance.
Example:
<div style="color: red; font-size: 16px;">This is red text</div>Effect:
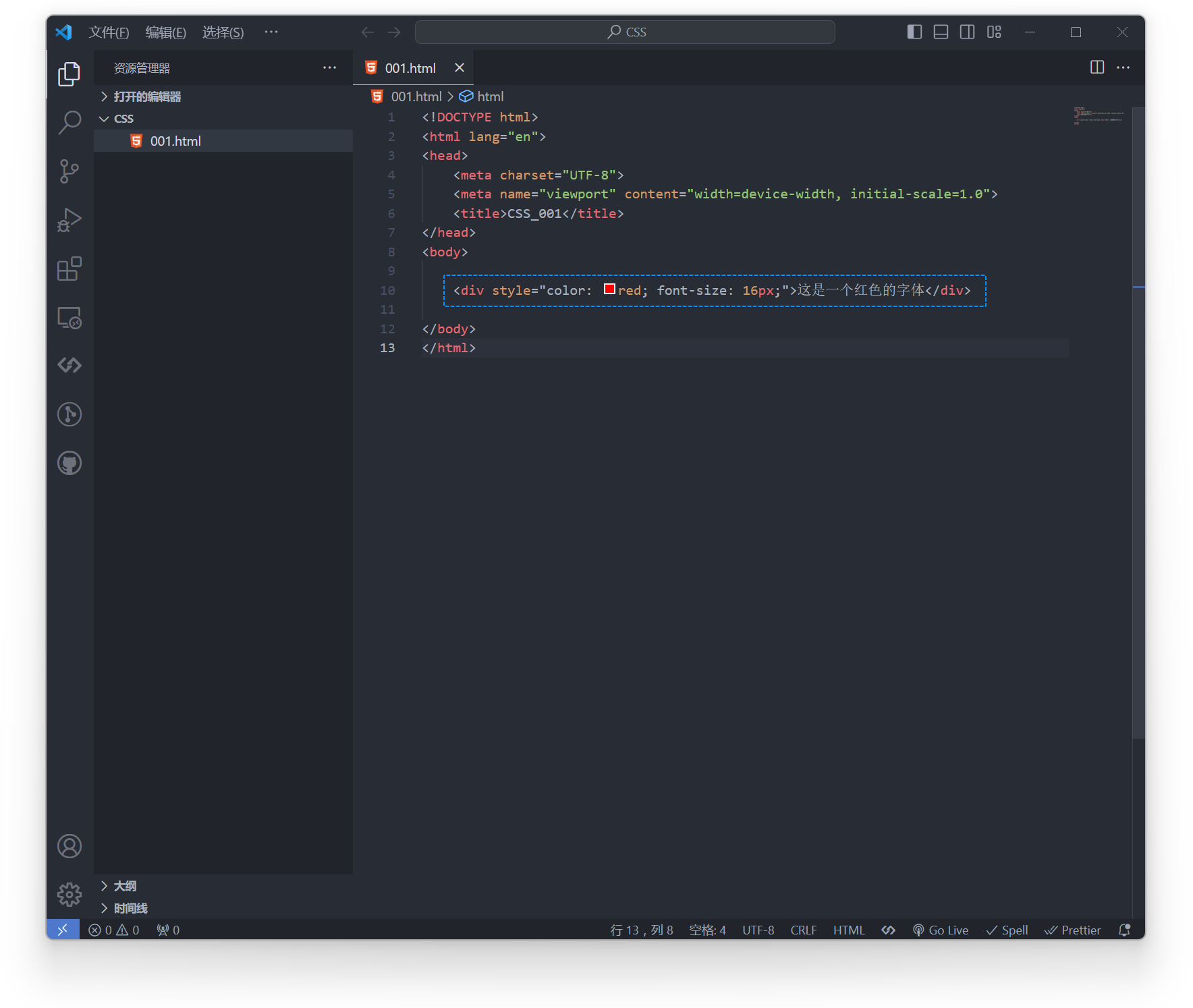
Internal Reference:
Write CSS code in the <style> tag, placed inside the <head> tag.
Internal reference is a relatively compromise approach of writing style code in the style tag of HTML files. The advantage of internal reference is that styles and HTML files are separated, making maintenance easier. Additionally, internal references can use browser caching to improve loading speed. However, internal references also have the following disadvantages:
- Page loading requires additional network requests, relatively less efficient.
- Styles and HTML files still have some coupling.
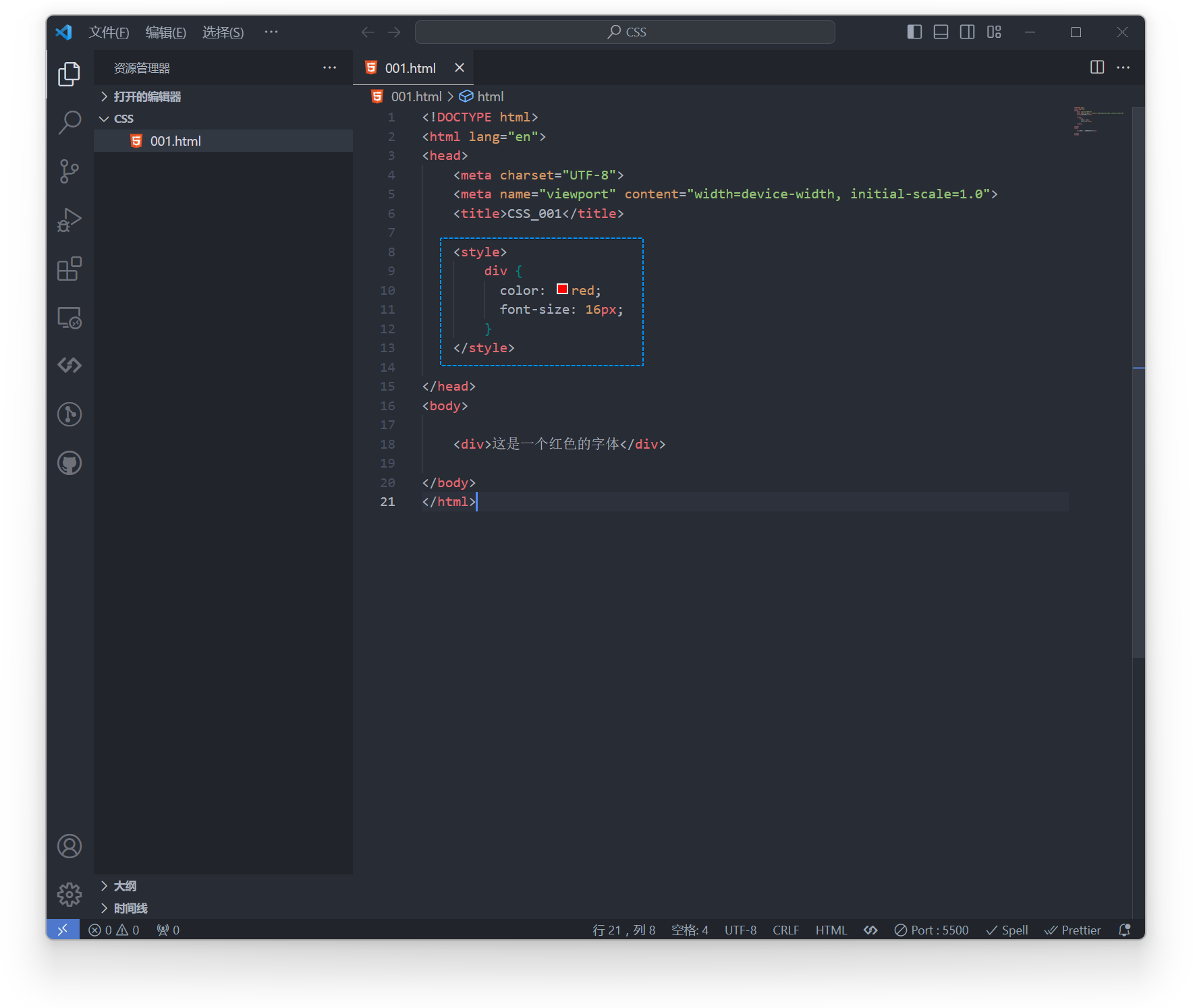
Example:
div { color: red; font-size: 16px;} <div>This is red text</div>Effect:
External Reference:
Write CSS code in a separate CSS file, then use the link tag to include it.
External reference is a more standard method of writing style code in separate CSS files. The advantage of external reference is that styles and HTML files are completely separated, making maintenance easier. Additionally, external references can be accelerated through CDN to improve file loading speed. External references also support compression and merging to reduce file size. However, external references also have the following disadvantages:
- Page loading requires additional network requests, but can be optimized.
- Depends on external resources, may cause blocking or loading failures.
- May require multiple requests for external files during development.
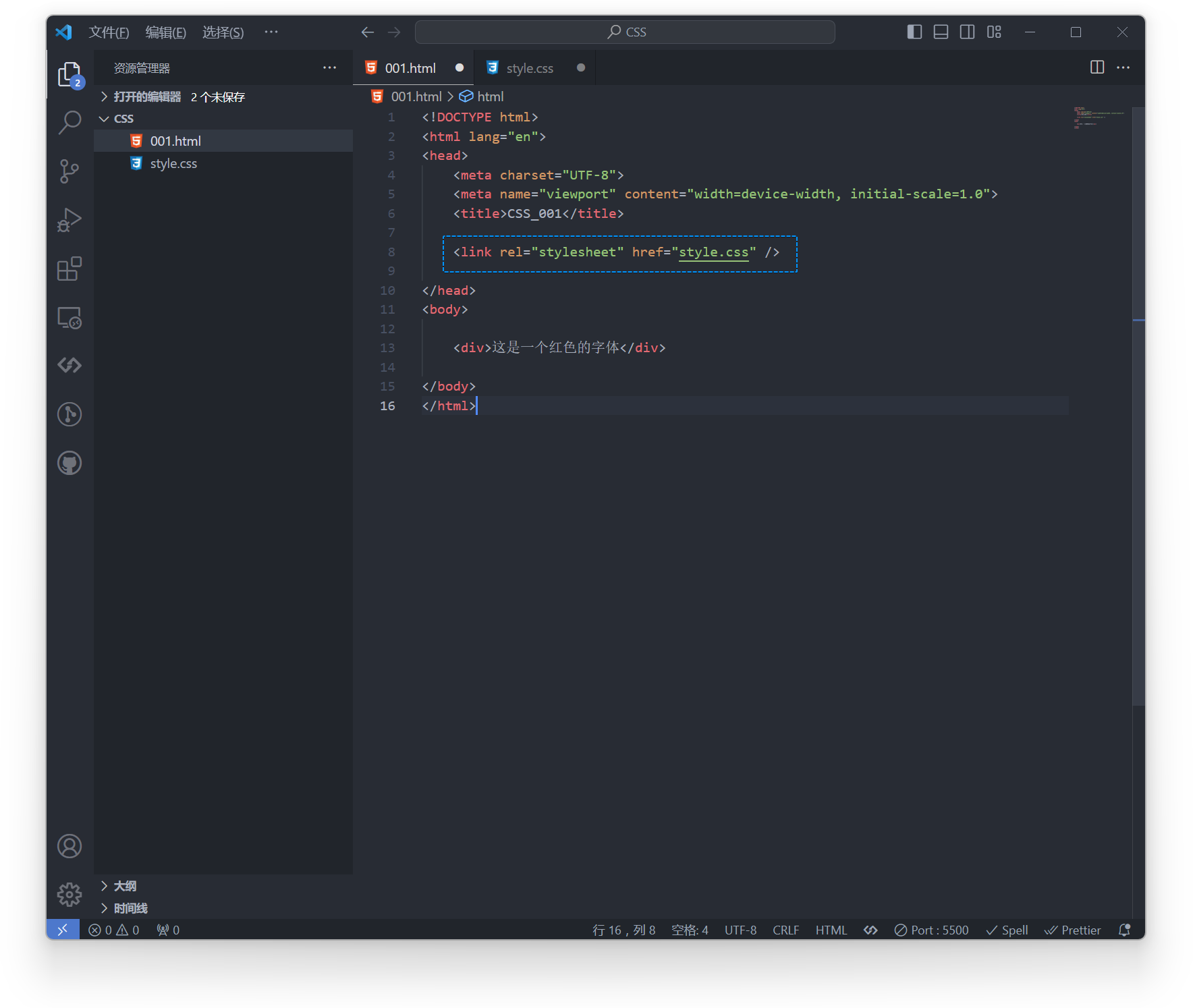
Example:
<head>
<!-- In the current directory, reference the stylesheet file in the subfolder styles --><link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<!-- In the current directory, reference the stylesheet file in the subfolder general within the subfolder styles --><link rel="stylesheet" href="/style.css" />
<!-- In the parent directory of the current directory, reference the stylesheet file in the subfolder styles --><link rel="stylesheet" href="../styles/style.css" />
</head>div { color: red; font-size: 16px;}Effect:
Cascading Order and Priority
CSS Cascading Order and Specificity are two key factors that determine CSS display style effects.
Cascading Order: CSS cascading order defines the weight of style rules, from high to low:
- Importance (!important): Style rules declared with !important have the highest priority. But should be used sparingly, as overuse leads to maintenance difficulties.
- Author Styles: Styles defined by web developers, including external stylesheets, internal stylesheets, and inline styles. Priority is between user styles and user agent styles.
- User Styles: Styles set by users through browser plugins or user settings, higher priority than user agent styles, such as font plugins.
- User Agent Styles: Browser’s default styles, with the lowest priority, such as fonts.
Priority: When there are multiple same-level or conflicting style rules, CSS displays style effects according to priority.
- Inline Styles: Styles specified within HTML tags have the highest priority.
- ID Selector (id): Styles specified through ID selectors, such as: #header.
- Class Selector, Attribute Selector, and Pseudo-class Selector (class): Styles specified through class selectors, such as:
.container. Styles specified through attribute selectors, such as:[type="text"]. Styles specified through pseudo-class selectors, such as::hover. - Element Selector: Selectors that specify HTML element names, such as
div,p.
When priorities are the same, rules defined later have higher priority.
Example:
#header { color: red;}
.container p { color: blue;}
p { color: green;}CSS Inheritance
CSS inheritance refers to the characteristic of child elements inheriting some property values from parent elements. Inheritance is an important feature in CSS that can simplify style writing and improve code maintainability. Not all CSS properties can be inherited; only some properties are defined as inheritable.
CSS inherited properties mainly include:
- Text Properties: font-family, font-size, font-weight, font-style, color, text-decoration, text-align, line-height, letter-spacing, word-spacing
- Color Properties: background-color, border-color, color, outline-color
- Border Properties: border-width, border-style, border-color
- Box Model Properties: margin, padding, width, height, display, float, position, z-index
CSS properties that are not inherited include, for example, width, height, margin, padding and other box model-related properties, positioning (position), floating (float), clear float (clear) and other layout-related properties.
Common CSS Properties and Their Functions:
Basic Properties width, height: Set the width and height of elements. margin: Set the margin of elements. padding: Set the padding of elements. color, background-color: Set the color and background color of elements. font-size, font-family, font-weight, font-style: Set the font size, font family, font weight, and font style of elements.
Layout Properties display: Set the display mode of elements. float: Set the floating mode of elements. position: Set the position of elements. top, left, right, bottom: Set the top, left, right, and bottom positions of elements. z-index: Set the stacking order of elements.
Text Properties text-align: Set the text alignment of elements. text-decoration: Set the text decoration of elements. line-height: Set the line height of elements. font-variant: Set the font variant of elements. text-transform: Set the text transformation of elements. letter-spacing, word-spacing: Set the letter spacing and word spacing of elements.
Border Properties border: Set the border style of elements. border-width: Set the border width of elements. border-style: Set the border style of elements. border-color: Set the border color of elements. border-radius: Set the border radius of elements.
Background Properties background: Set the background of elements. background-color: Set the background color of elements. background-image: Set the background image of elements. background-repeat: Set the background image repeat mode of elements. background-position: Set the background image position of elements. background-size: Set the background image size of elements.
Transition Properties transition: Set the transition effect of elements. transition-property: Set the transition property of elements. transition-duration: Set the transition duration of elements. transition-timing-function: Set the transition timing function of elements. transition-delay: Set the transition delay of elements.